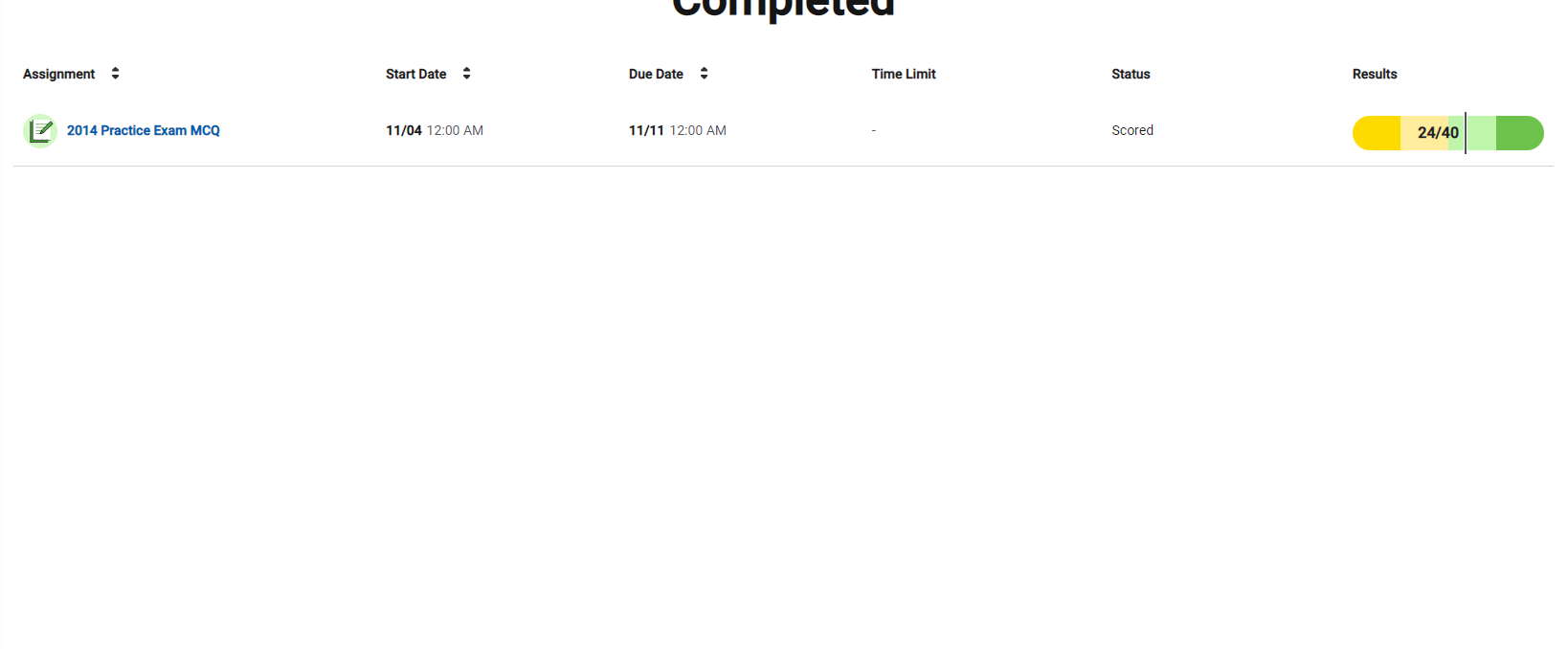
MCQ2014
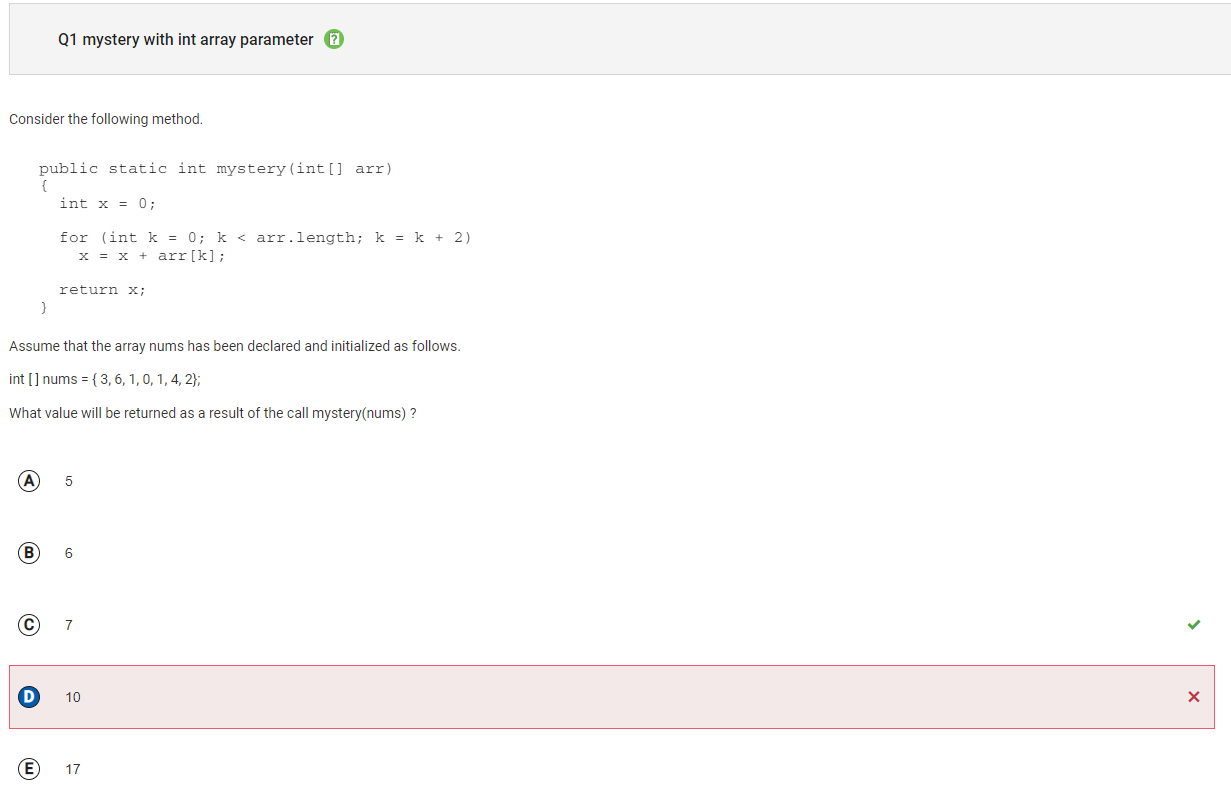
Q1
 ```
```
Answer D Incorrect. This would be the result if k was initialized to 1 instead of 0.
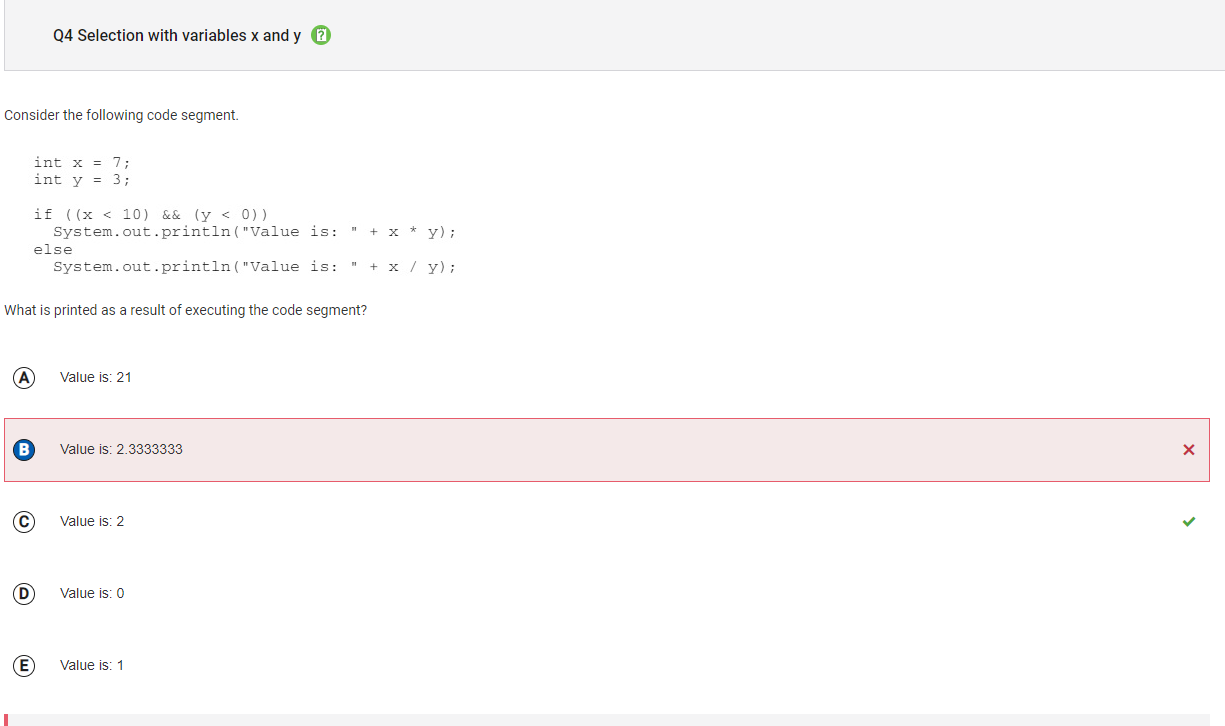
```Q4
 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. This would be the result if the division used was floating point division, instead of integer division. This would be the case if either x or y were of type double instead of type int or if either value was typecast as a double in the expression.
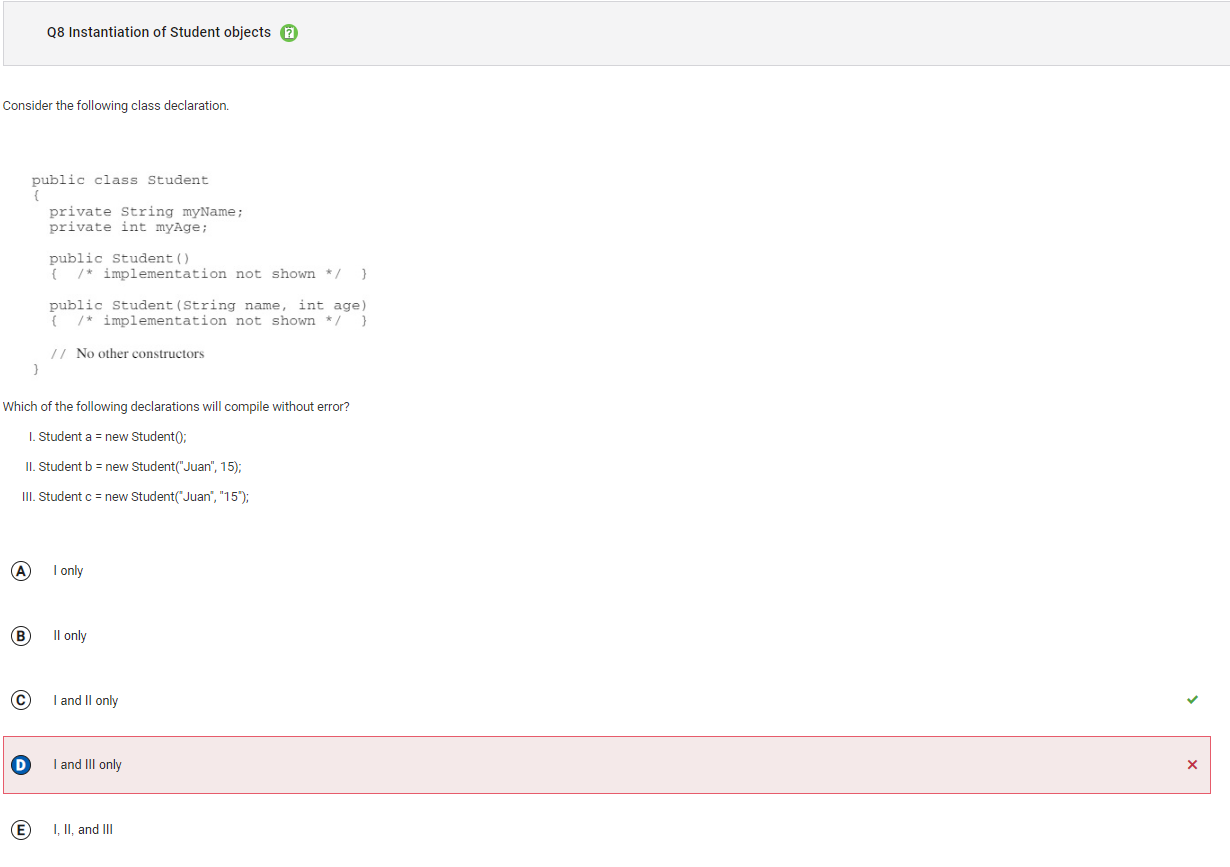
```Q8
 ```
```
Answer D Incorrect. Choice II will also compile as it uses the two-parameter constructor, with the parameters in the order of String then int, to create a new Student object and assign it to variable b of type Student. Choice III attempts to use the two-parameter constructor, however the order of the parameters is a String followed by a String (since both parameters are in quotations). There is no two-parameter constructor with two String parameters. This statement will cause a compile time error.
```Q10
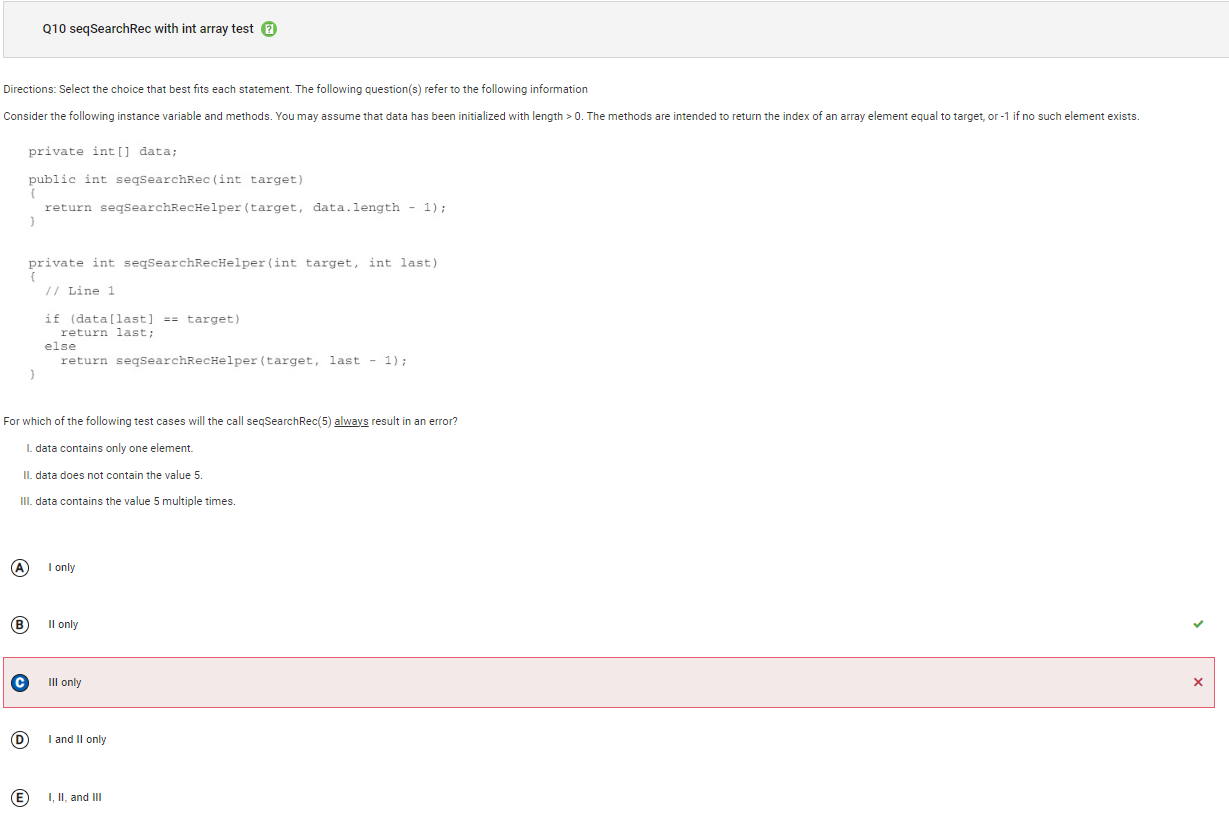 ```
```
Answer C Incorrect. Choice II will eventually cause an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException to be thrown when the recursive call is made with target and -1. This will happen after every valid index in data has been examined. During this call, data[-1] is out of bounds. Choice III will correctly return the index of the element closest to the end of the array with the value target, since data[last] == target will be true at some valid index value of last.
```Q12
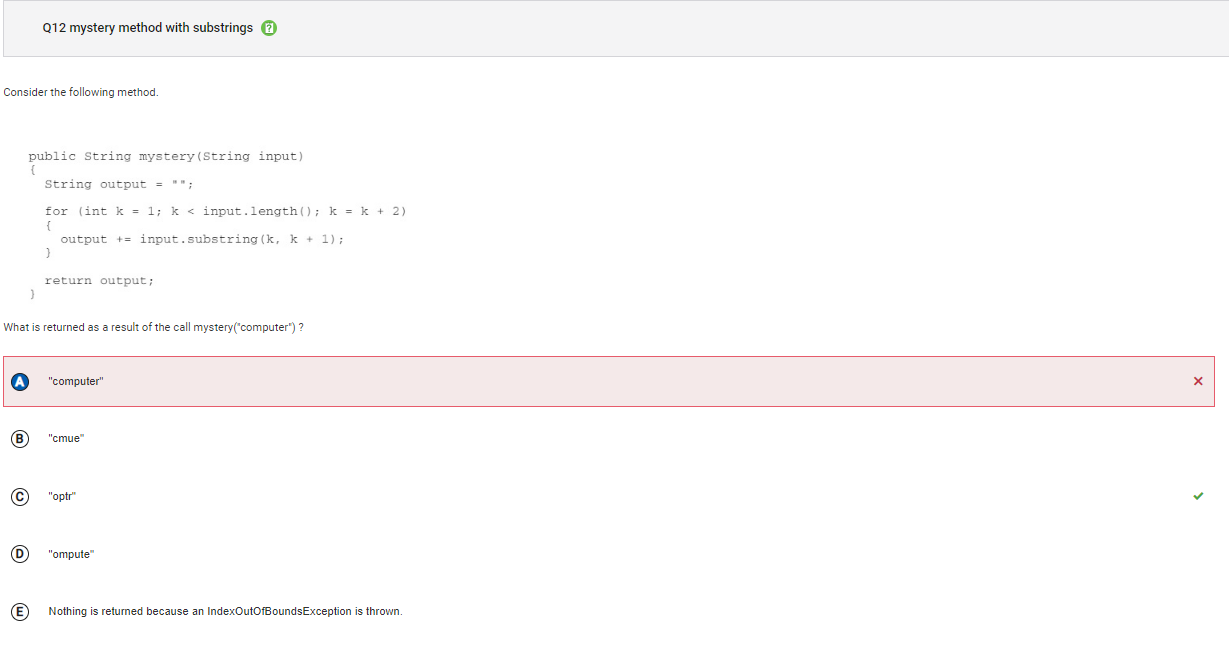 ```
```
Answer A Incorrect. This would be the return value if k started at 0 and was incremented by 1.
```Q14
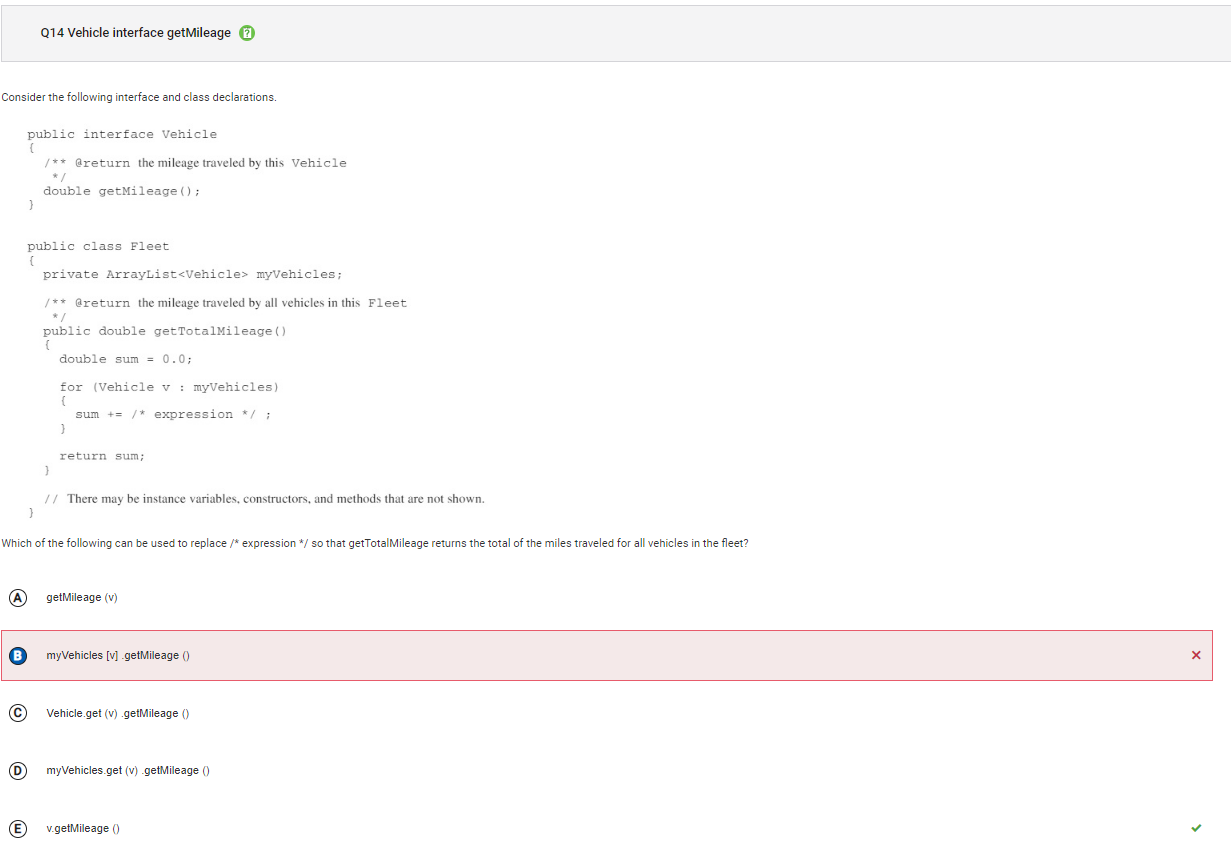 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. The access being used here is what would be used if myVehicles was an array instead of an ArrayList and v was an index of the myVehicles array. However, in this case an enhanced for loop is being used, which accesses the elements of myVehicles directly and assigns v the value of the elements. Please note that interface is no longer a part of the AP CSA exam.
```Q15
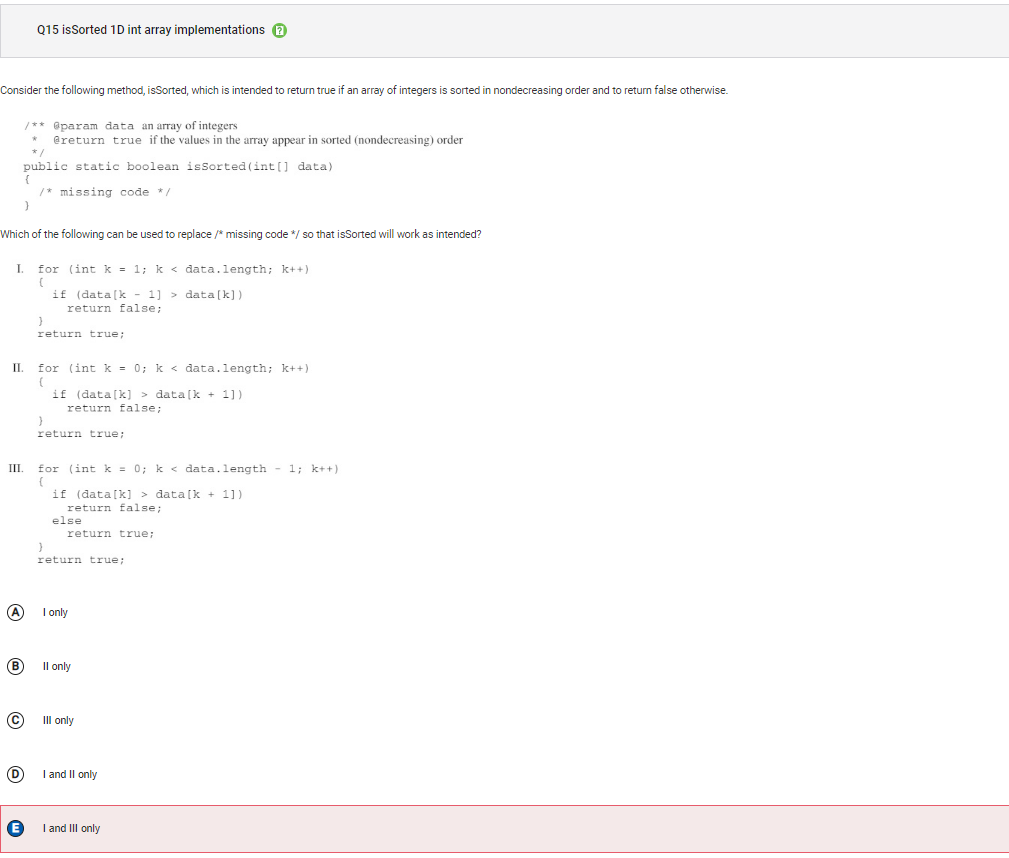 ```
```
Answer E Incorrect. Choice III has a loop control variable k that starts at 0, increments by 1, and will terminate the loop when k has the value data.length – 1. In each iteration, there is a check to see if the current value is larger than the subsequent value. If it is, false is returned because elements would not be nondecreasing, otherwise true is returned. As a result, only data[0] and data[1] are examined. The remaining elements in data are not checked because the method will stop once a return statement is reached. This means that the method could return true even when there are consecutive elements in data that are nondecreasing.
```Q16
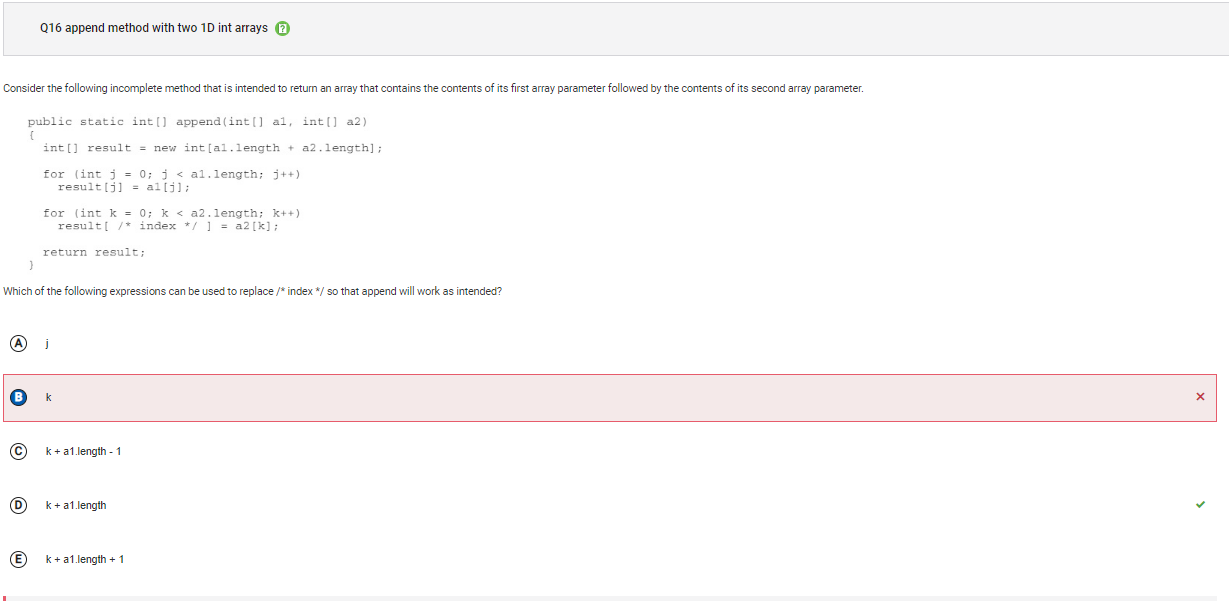 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. Using the value of k will mean that some or all of the elements from a1 will not be in result as they will be replaced with a2 values. In the first for loop, result[0] was assigned a1[0]. In the second loop, when k has the value 0, result[0] will be assigned a2[0].
```Q19
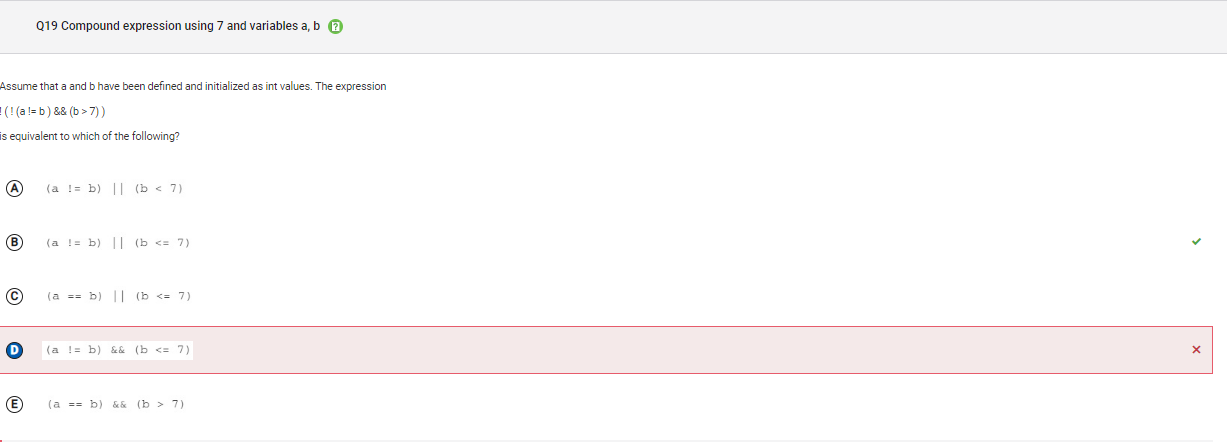 ```
```
Answer D Incorrect. When you apply De Morgan’s Law the logic operator and (&&) becomes an or (||) and vice versa.
```Q20
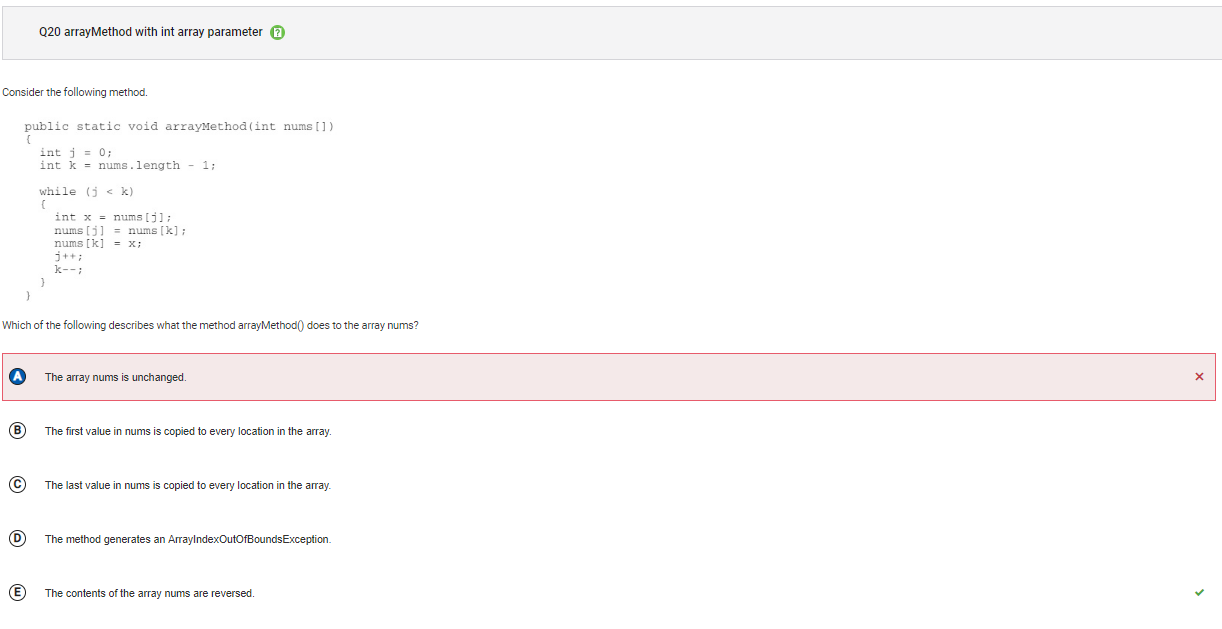 ```
```
Answer A Incorrect. Since the while loop terminates when j is greater than or equal to k, the first half of the elements in nums are swapped with the second half of the elements in nums. If the while condition was changed to j < nums.length, then all the elements would be swapped and then swapped back to their original location and nums would be unchanged.
```Q23
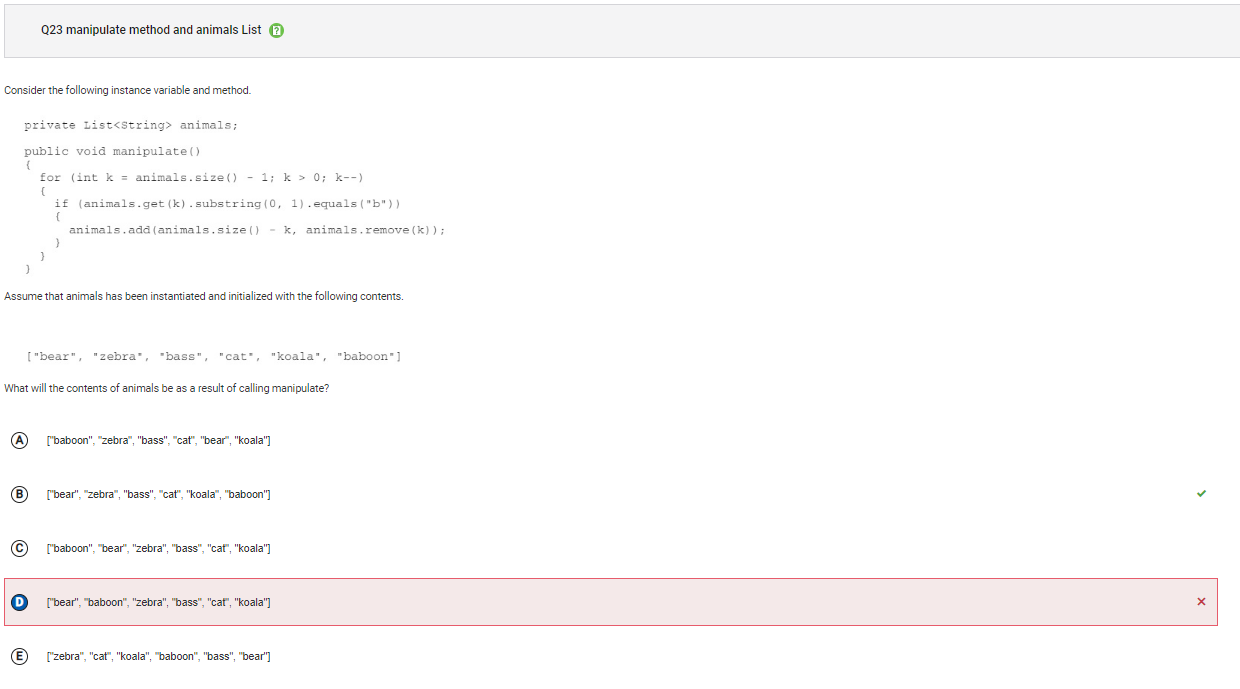 ``
``
Answer D Incorrect. List is an interface, which an ArrayList implements. Please note that List is no longer tested as part of the AP CSA exam and ArrayList will be used instead. This would be the case if the loop condition was k > 1 rather than k > 0.
```Q25
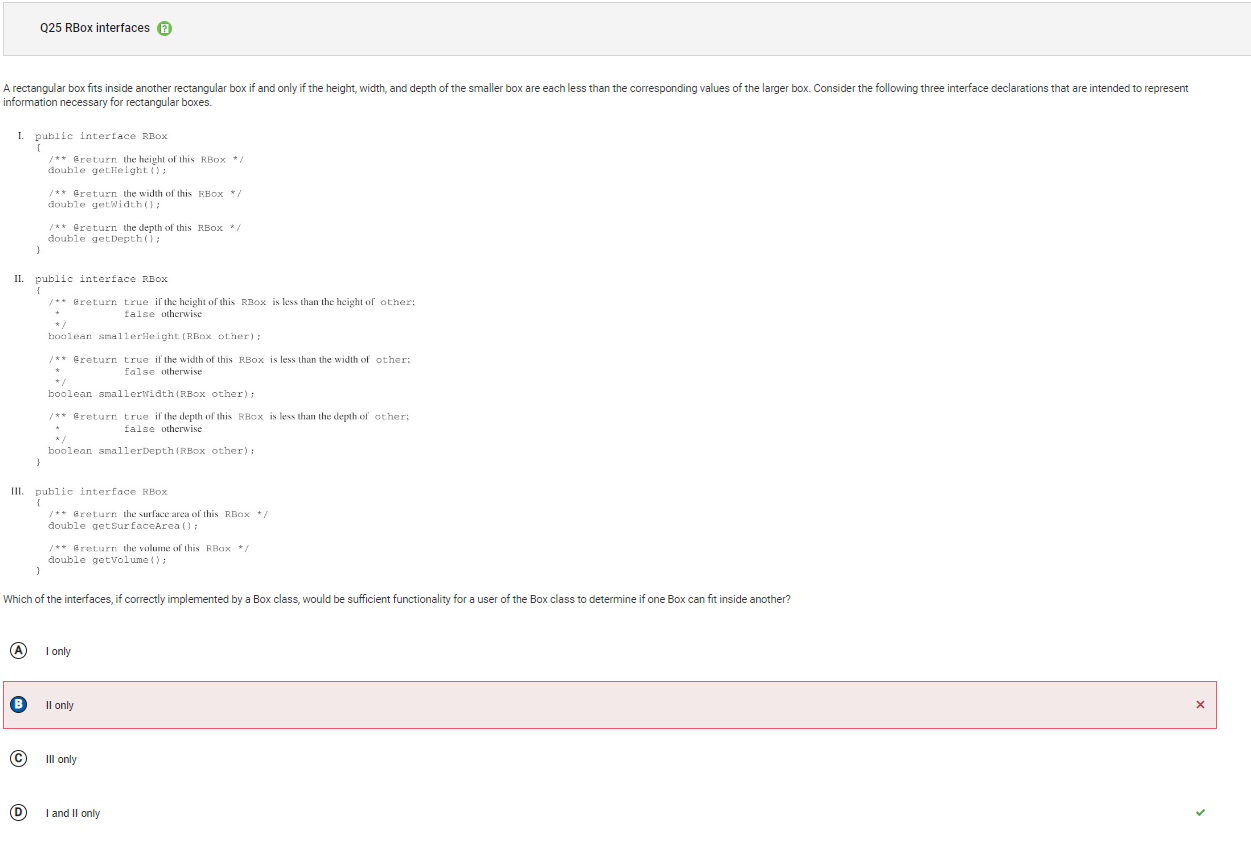 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. Please note that interface is no longer a part of the AP CSA exam. Choice I provides the user access to the height, width, and depth of a box through the accessor methods getHeight, getWidth, and getDepth. This allows comparisons to be made in each of the three dimensions to determine if one box can fit inside another box.
```Q28
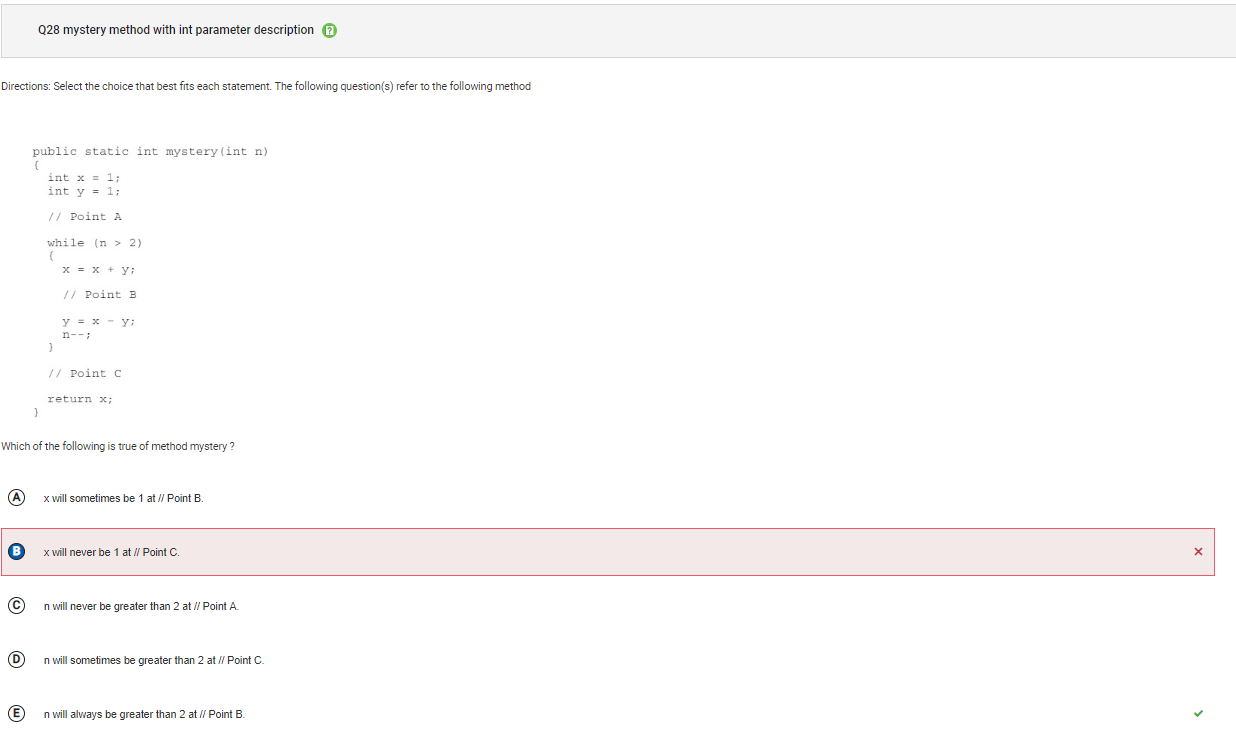 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. If the value of n is 2 or less in the original call to the method mystery, the loop will be skipped and x will be 1 at //Point C.
```Q30
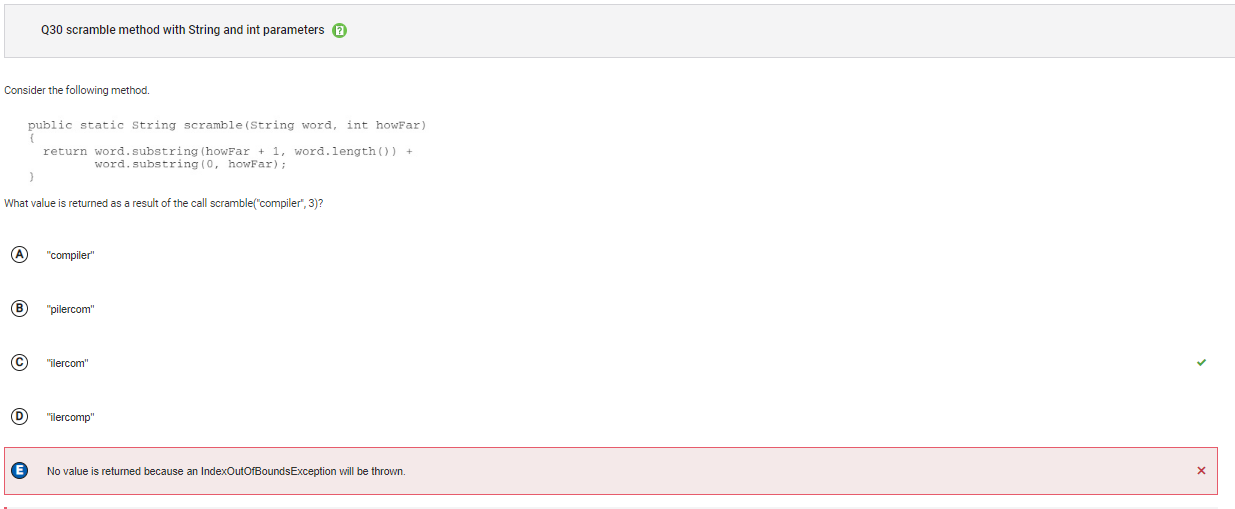 ```
```
Answer E Incorrect. Since the two parameter substring method returns the substring beginning at the first parameter and ending at the second parameter – 1, no IndexOutOfBoundsException will be thrown. The indices 4, 7 (in the first call to substring), 0 and 2 (in the second call to substring) are all valid indices in "compiler".
```Q34
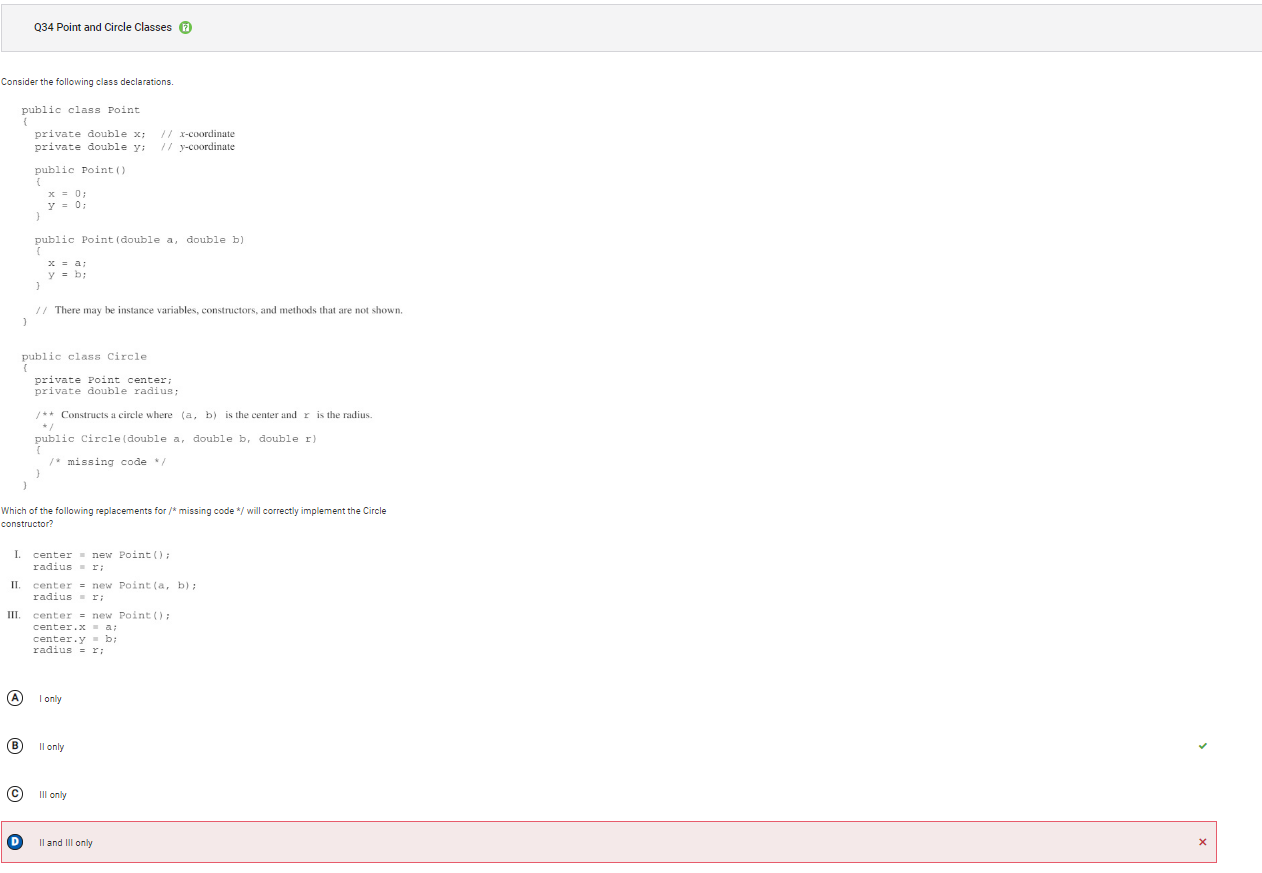 ```
```
Answer D Incorrect. Choice III uses the default Point constructor to assign center a new Point with x and y both equal to 0. It attempts to update x and y, however since they are private instance variables in Point, they are not able to be accessed directly in Circle. This code will cause a compile time error.
```Q39
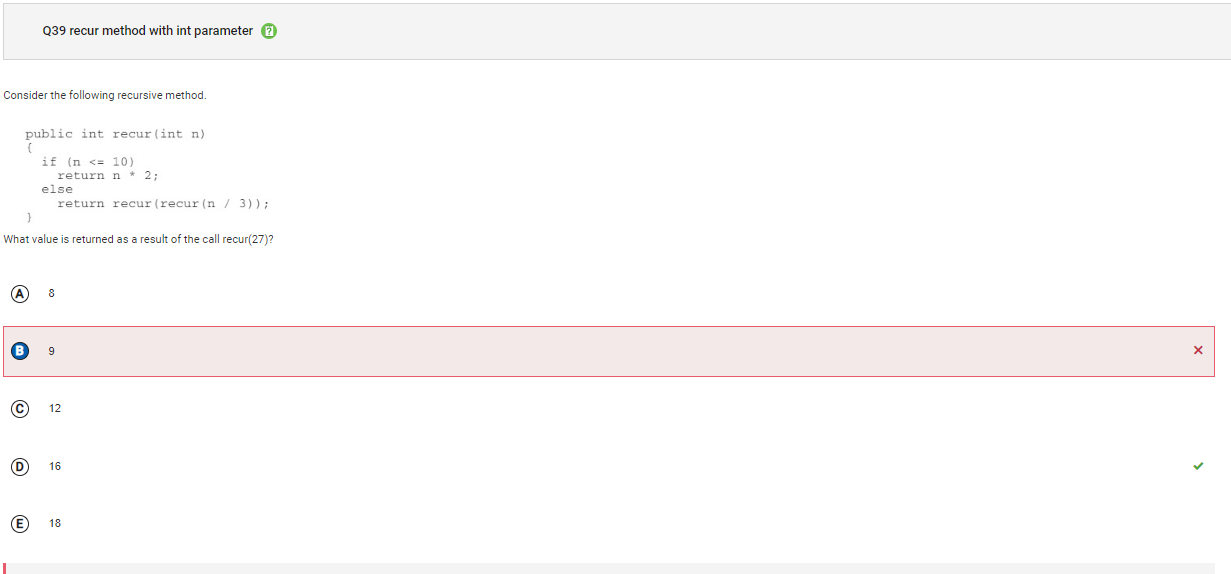 ```
```
Answer B Incorrect. This is the value that is passed in the first recursive call to recur.
```Collegeboard 66 Qs
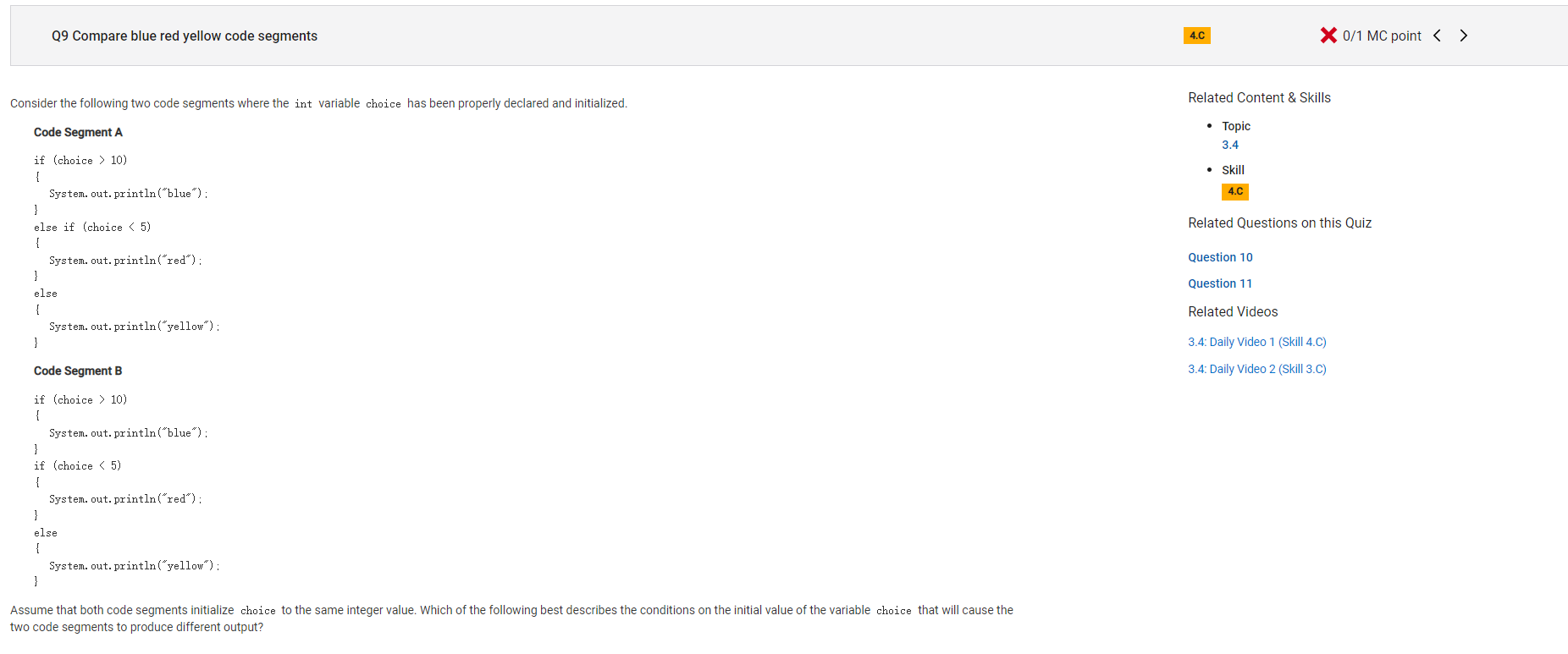
 ```
```
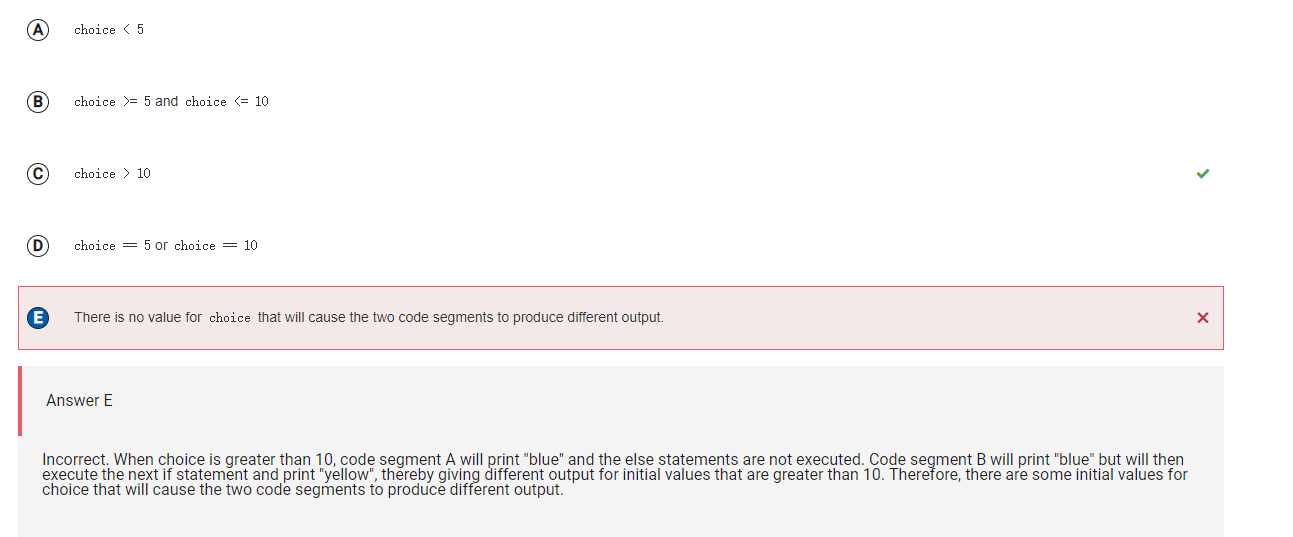
Answer E
Incorrect. When choice is greater than 10, code segment A will print "blue" and the else statements are not executed. Code segment B will print "blue" but will then execute the next if statement and print "yellow", thereby giving different output for initial values that are greater than 10. Therefore, there are some initial values for choice that will cause the two code segments to produce different output.
Correct Answer: C
Reason: When choice is greater than 10, code segment A will print "blue" and the else statements are not executed. Code segment B will print "blue" but will then execute the next if statement and print "yellow", thereby giving different output for initial values that are greater than 10.
```
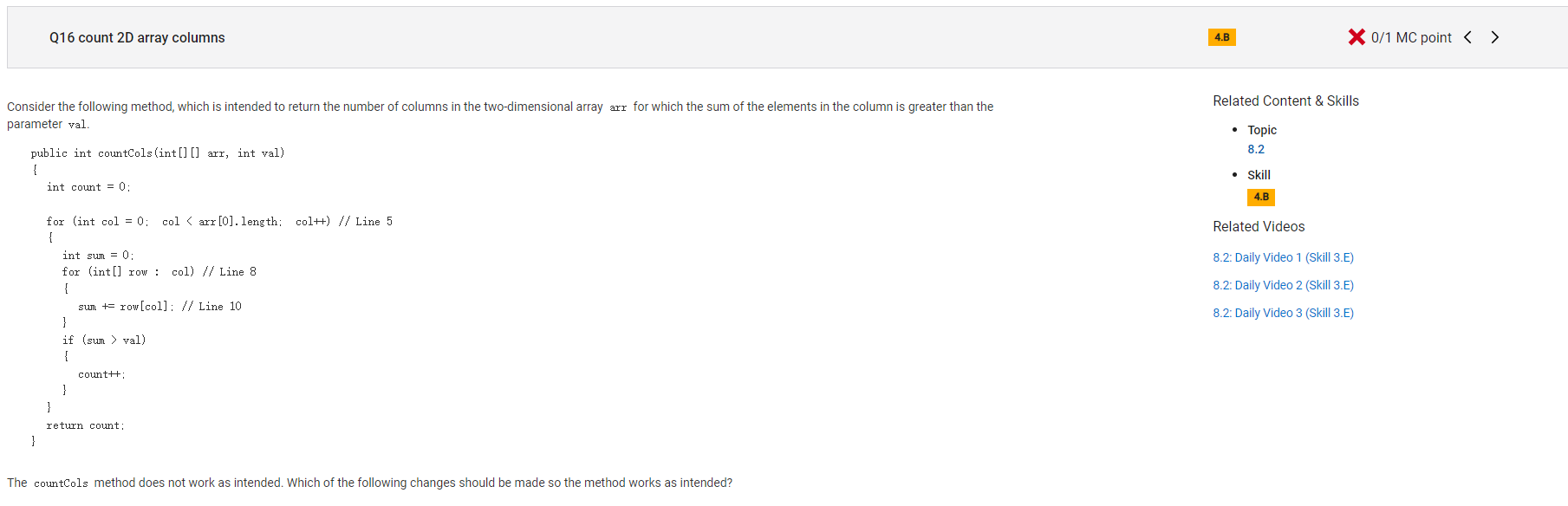
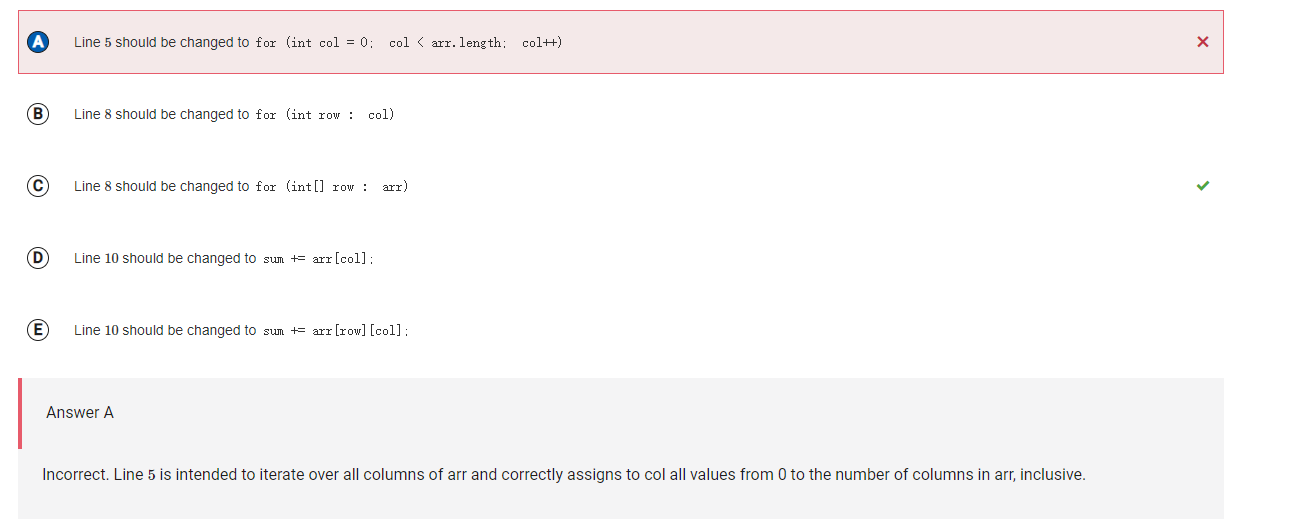 ```
```
Answer A
Incorrect. Line 5 is intended to iterate over all columns of arr and correctly assigns to col all values from 0 to the number of columns in arr, inclusive.
Correct Answer: C
Reason: Two-dimensional arrays are stored as arrays of one-dimensional arrays. Line 8
is intended to assign to row, a one-dimensional array of int values, a single row of the two-dimensional array arr. The original version of line 8
attempts to assign a row of col, but col is not a two-dimensional array.
```
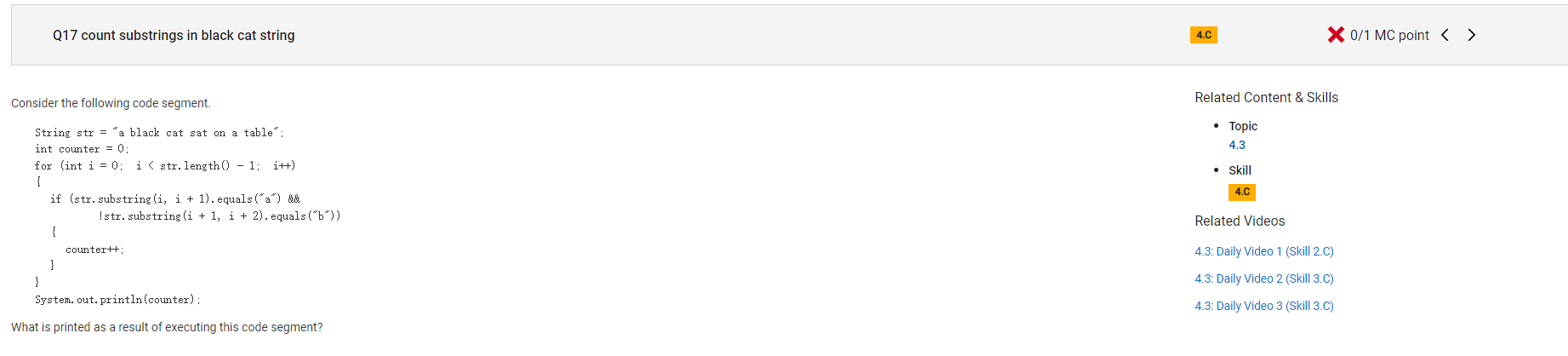
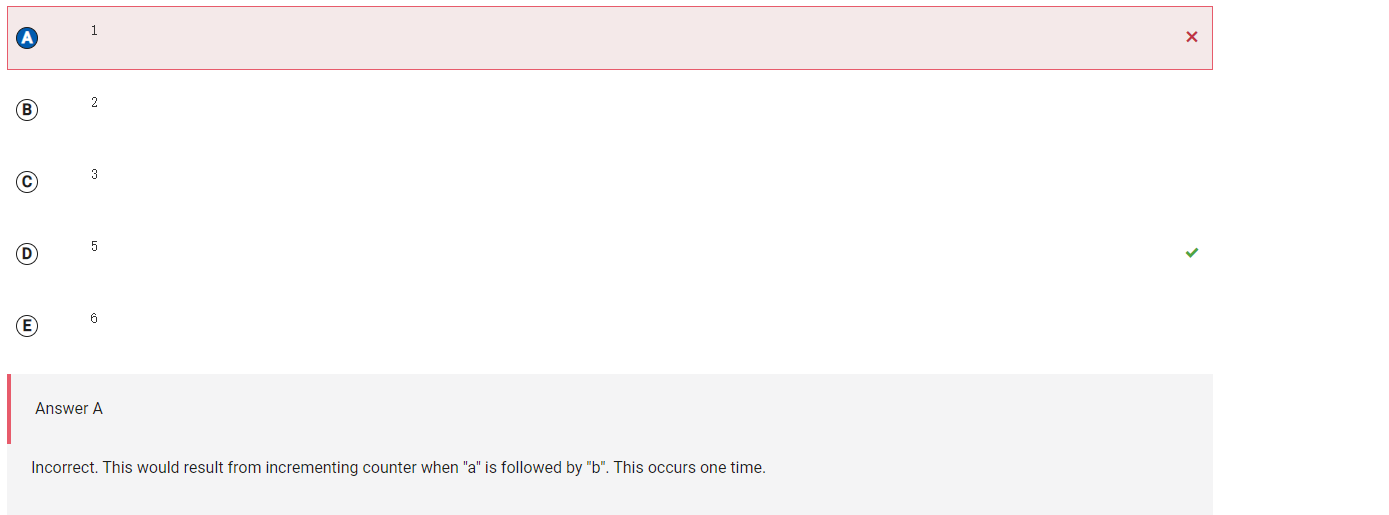 ```
```
Answer A
Incorrect. This would result from incrementing counter when "a" is followed by "b". This occurs one time.
Correct Answer: D
Reason: The expression str.substring(i, i + 1).equals("a") will evaluate to true if str contains the string "a" at position i. The expression !str.substring(i + 1, i + 2) will evaluate to true if str does not contain the string "b" at position i + 1. The variable counter is incremented when both of those expressions evaluate to true or, in other words, whenever "a" is not immediately followed by "b". This occurs five times in the given string: "a ", "ac", "at", "at", and "a ".
```
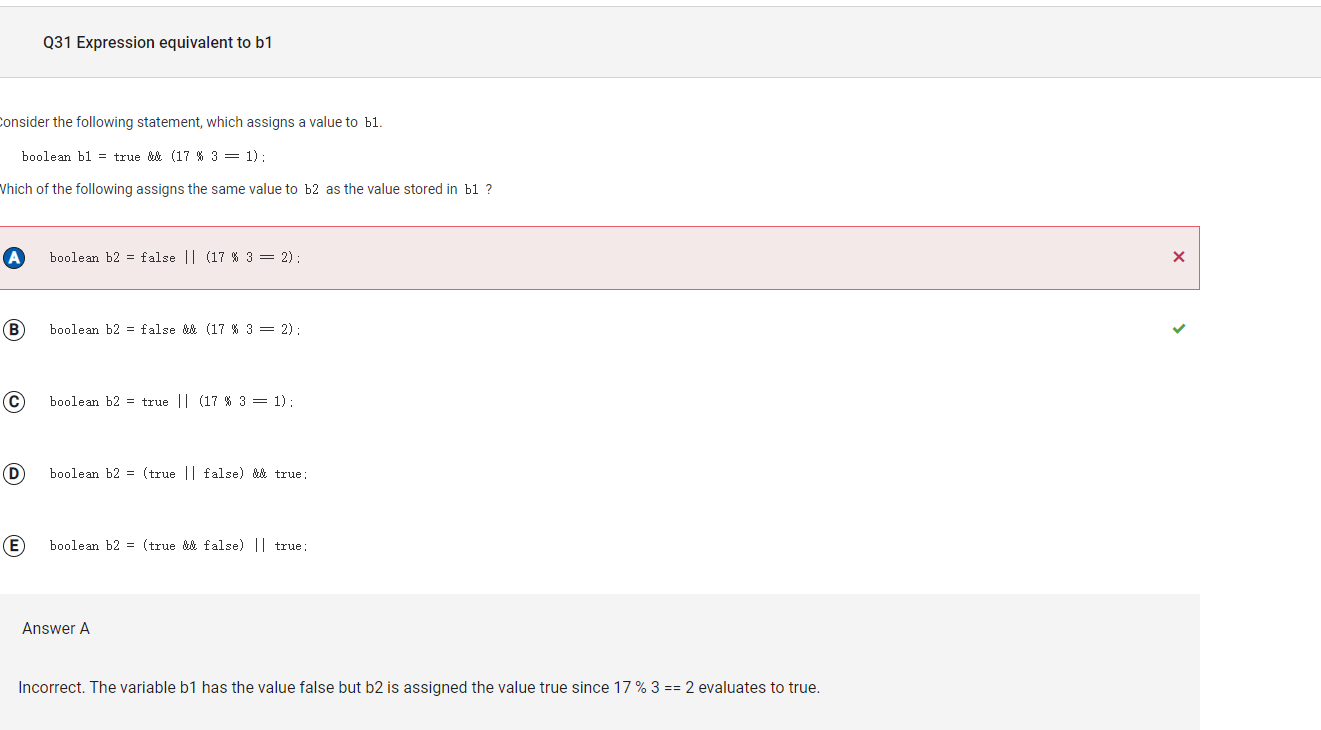 ```
```
Answer A
Incorrect. The variable b1 has the value false but b2 is assigned the value true since 17 % 3 == 2 evaluates to true.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: The expression 17 % 3 == 1 evaluates to false, and true && false evaluates to false, so b1 is assigned the value false. The expression on the right-hand side of the assignment statement for b2 evaluates to false by short circuit evaluation.
```
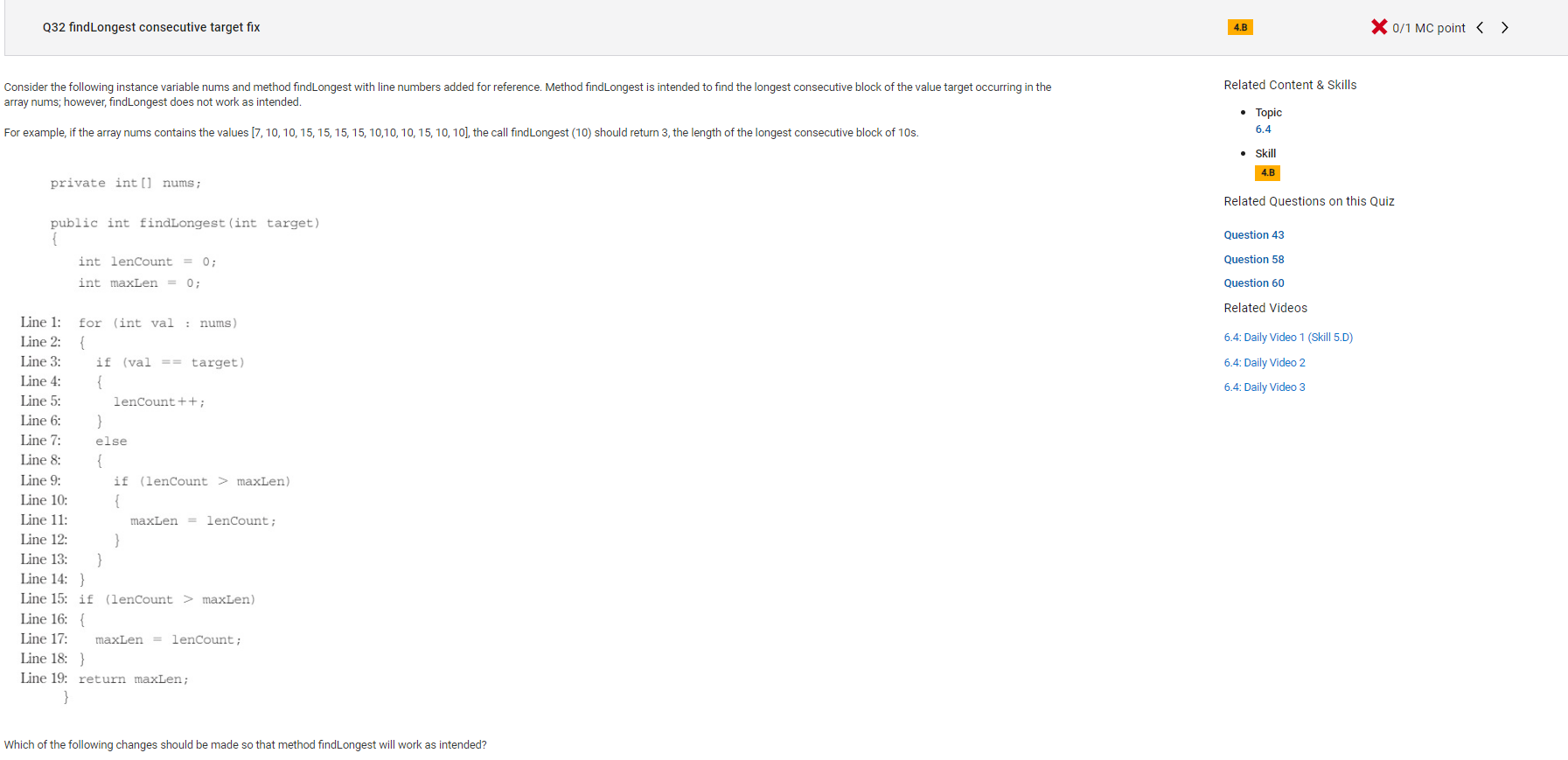
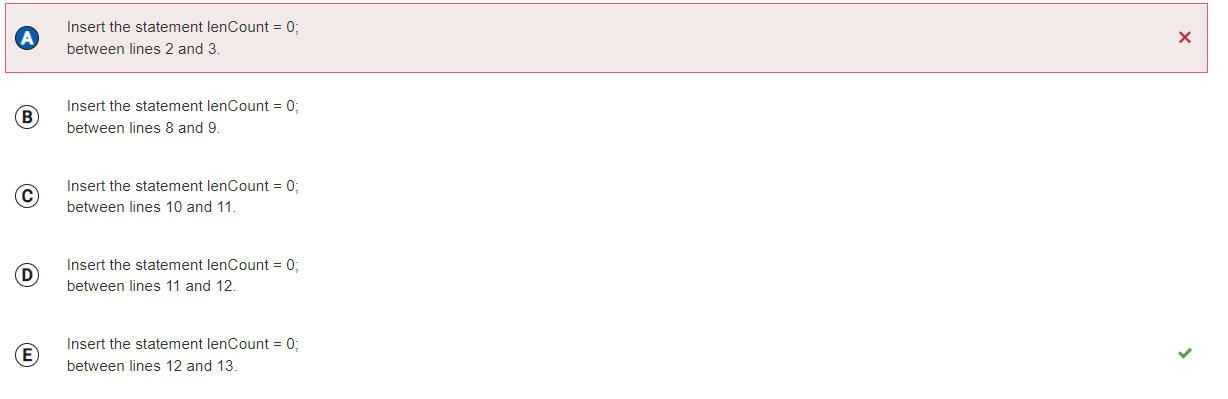 ```
```
Answer A
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: D
Reason: Still don't understand.
```
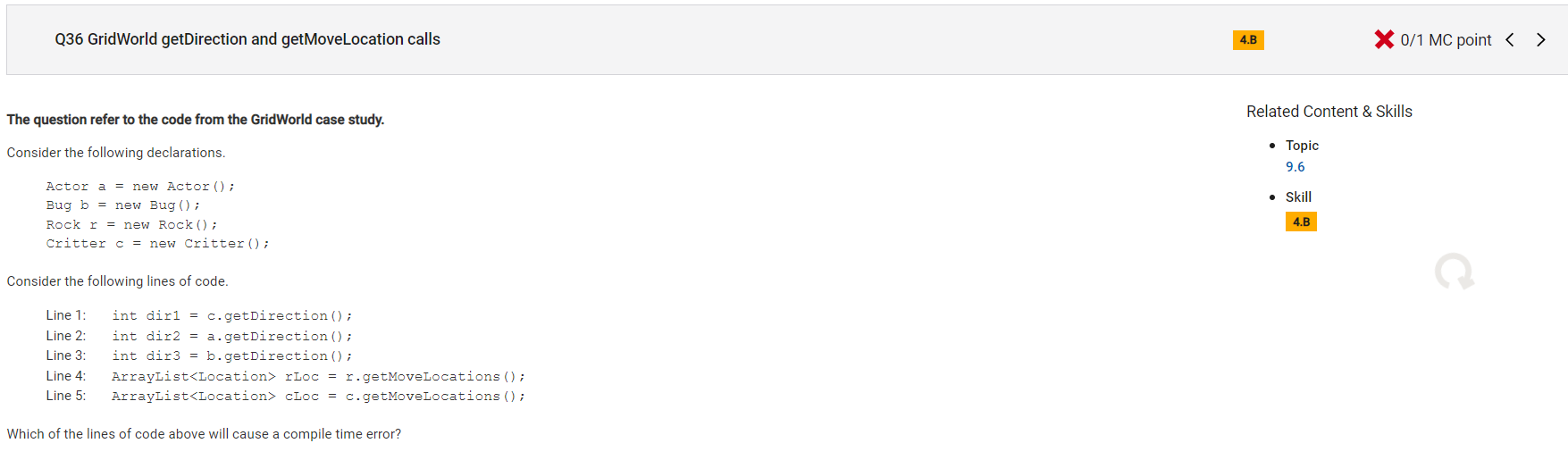
 ```
```
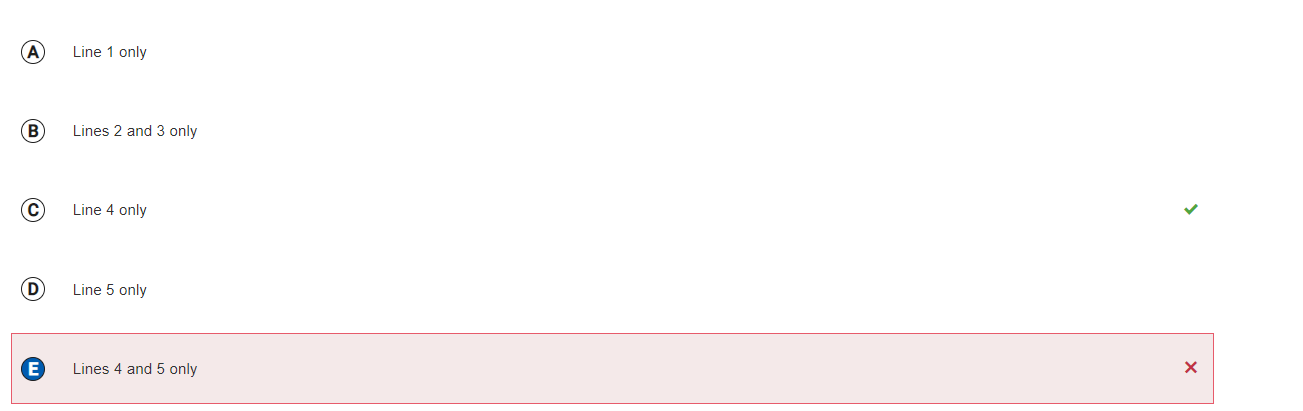
Answer E
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: C
Reason: Still don't understand, maybe because line 4 "r" has not been called in the method getDirection
```
 ```
```
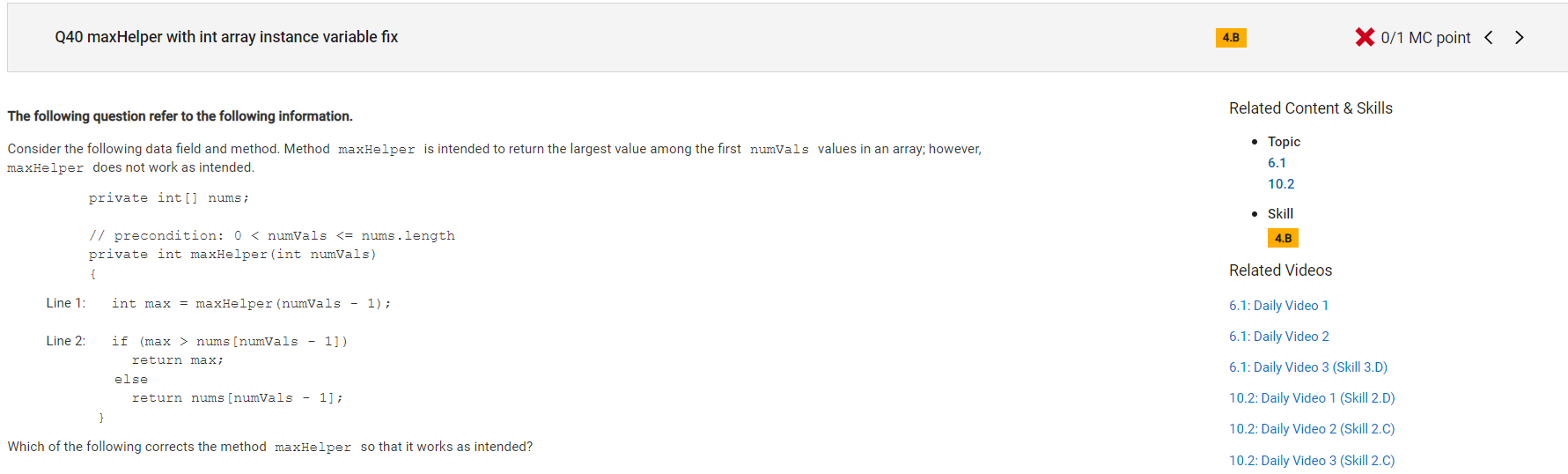
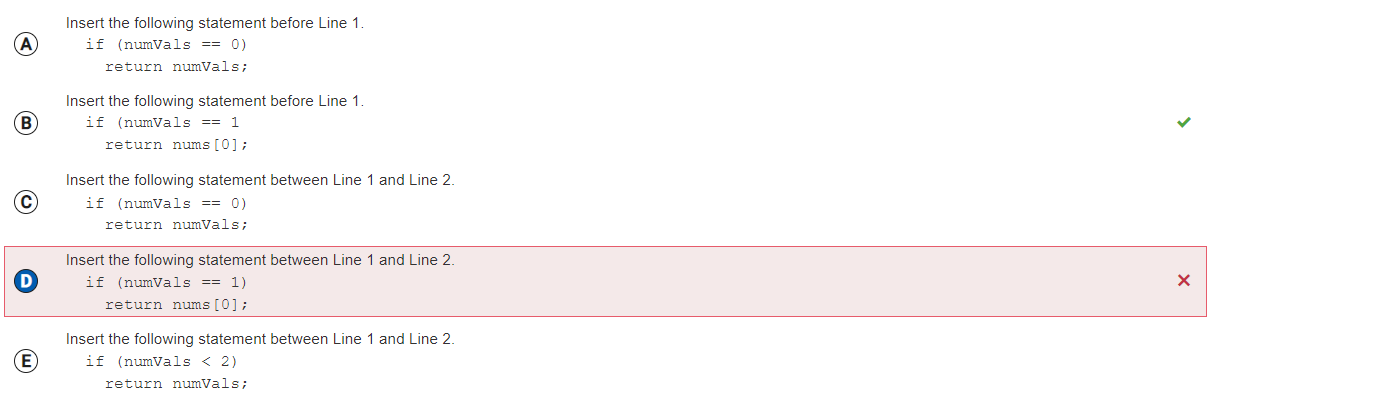
Answer D
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: Still don't understand
```
 ```
```
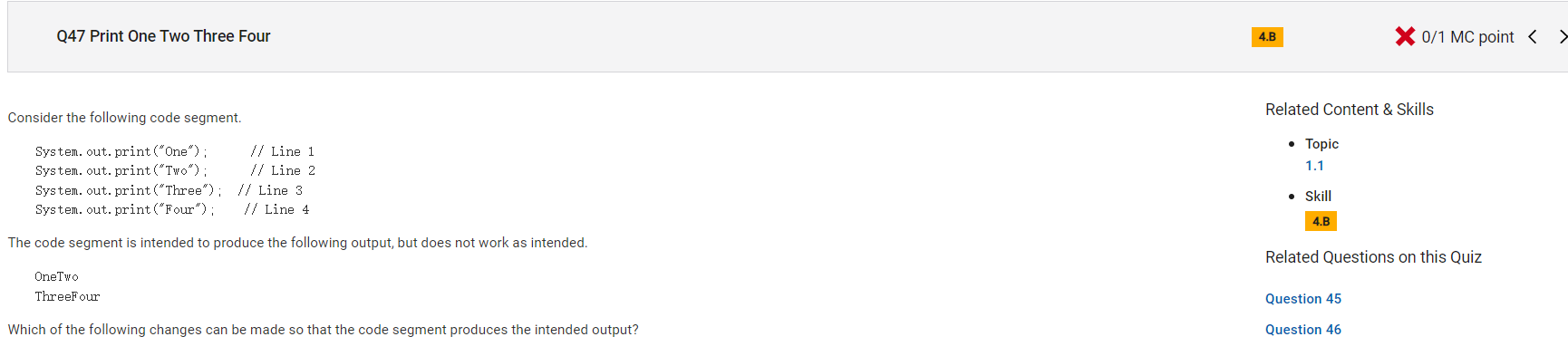
Answer C
Incorrect. This change would print "OneTwoThree" on the first line and "Four" on the second line.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: As is, the code segment prints all four strings on the same line. Changing print to println in line 2 will move the cursor to the next line after "Two" is printed.
```

 ```
```
Answer B
Incorrect. This method call returns false because the first character is lexicographically less than the second character of the string.
Correct Answer: D
Reason: If the first character of str is lexicographically greater than the second character of str, the method returns the result of the recursive call with a parameter that contains all but the first character of str. If the first character of str is lexicographically less than or equal to the second character of str, the method returns false. If no such character pair (where the first character of str is lexicographically less than or equal to the second character of str) is found, the base case is reached and the value true is returned.
```
 ```
```
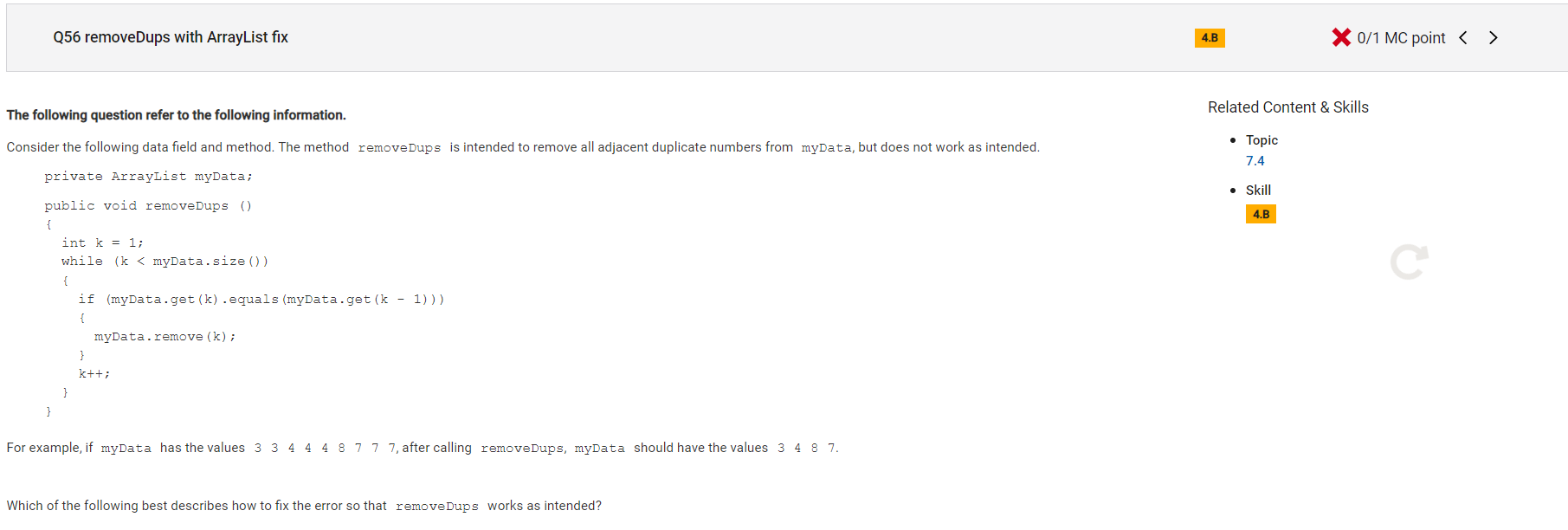
Answer D
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: E
Reason: that makes sense, only k++ when it doesn't remove the element.
```
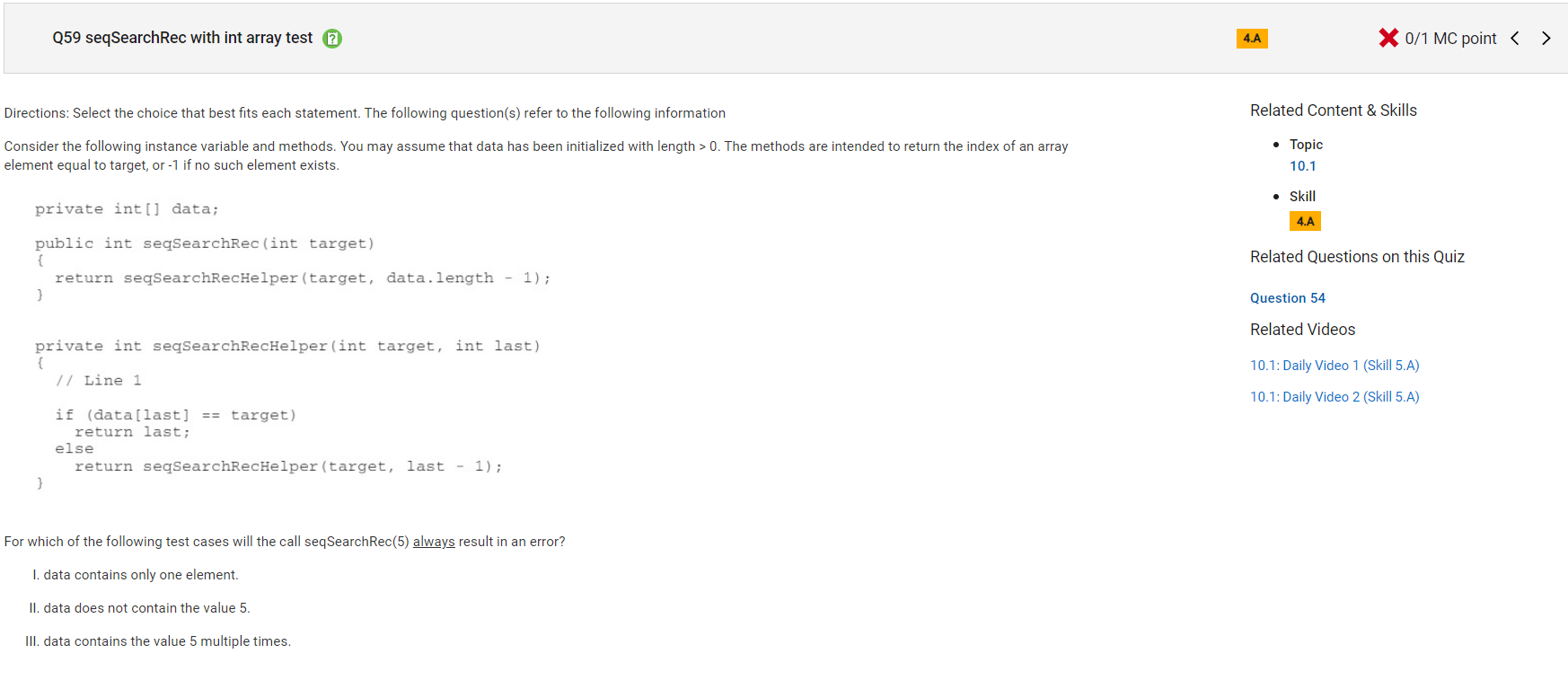
 ```
```
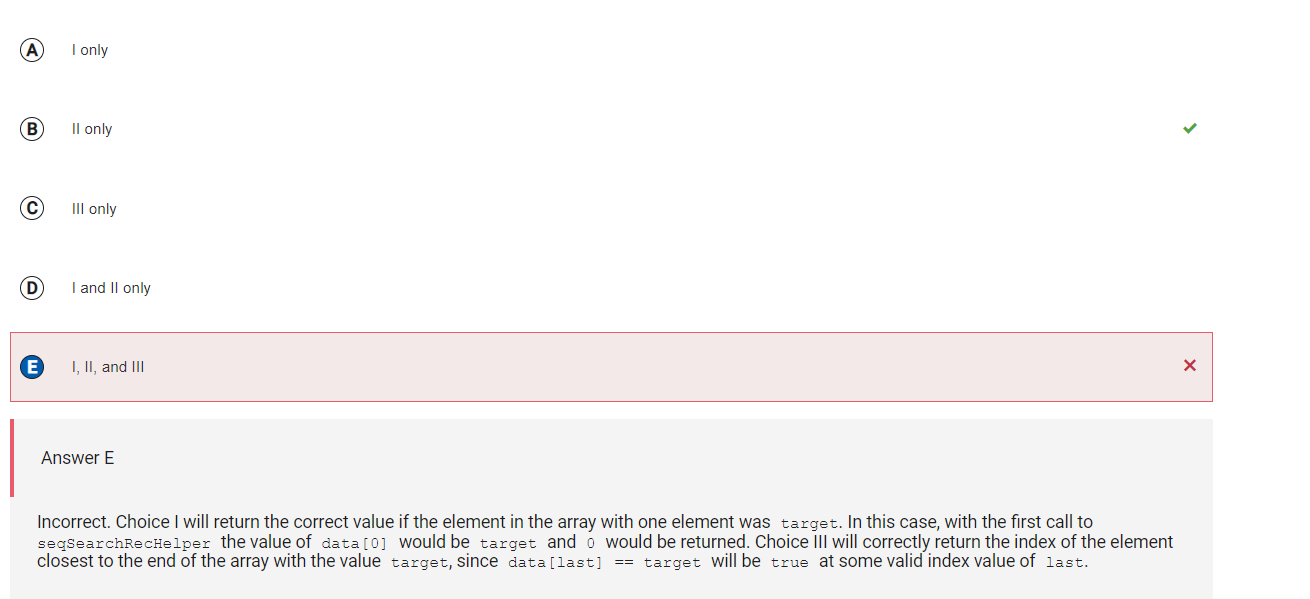
Answer E
Incorrect. Choice I will return the correct value if the element in the array with one element was target. In this case, with the first call to seqSearchRecHelper the value of data[0] would be target and 0 would be returned. Choice III will correctly return the index of the element closest to the end of the array with the value target, since data[last] == target will be true at some valid index value of last.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: Choice I will return the correct value if the element in the array with one element was target. In this case, with the first call to seqSearchRecHelper the value of data[0] would be target and 0 would be returned. Choice II will eventually cause an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException to be thrown when the recursive call is made with target and -1. This will happen after every valid index in data has been examined. During this call, data[-1] is out of bounds. Choice III will correctly return the index of the element closest to the end of the array with the value target, since data[last] == target will be true at some valid index value of last.
```
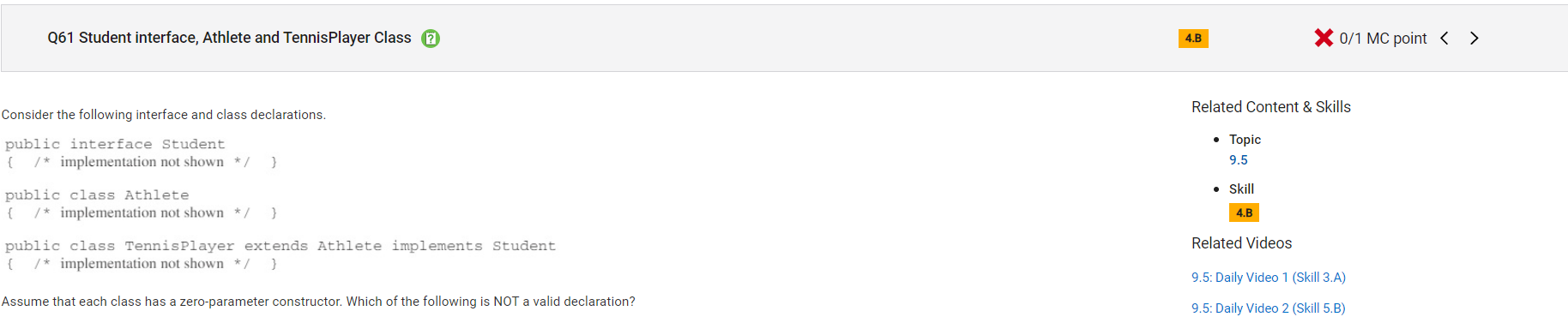
 ```
```
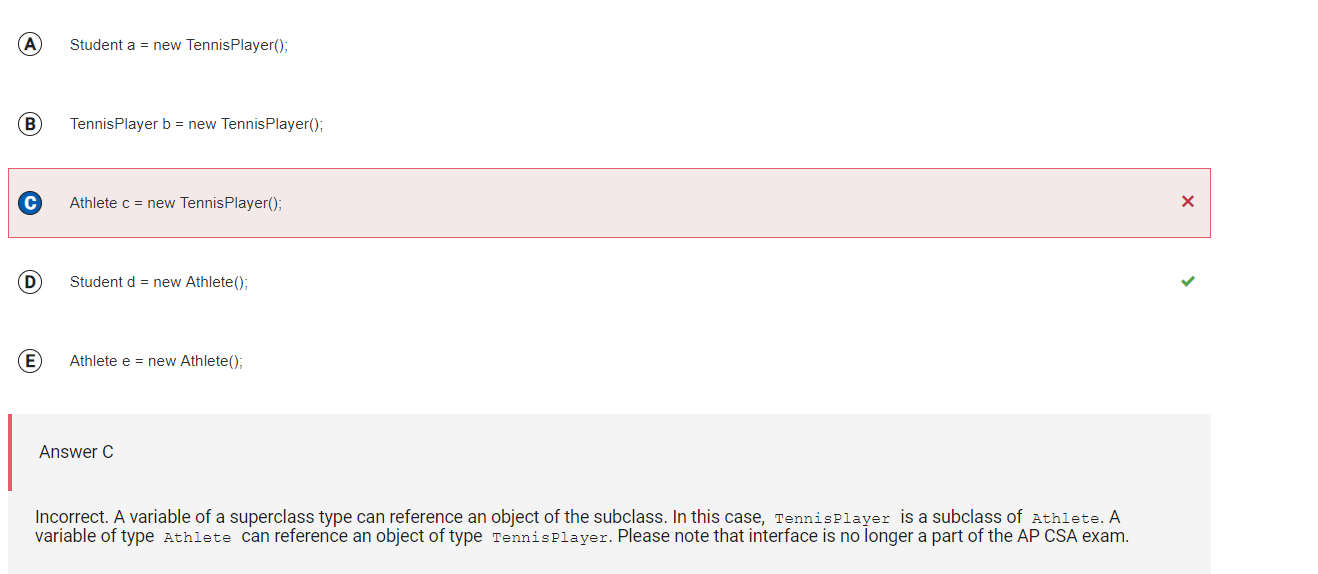
Answer C
Incorrect. A variable of a superclass type can reference an object of the subclass. In this case, TennisPlayer is a subclass of Athlete. A variable of type Athlete can reference an object of type TennisPlayer. Please note that interface is no longer a part of the AP CSA exam.
Correct Answer: D
Reason: Variables of type Student need to reference objects of types that implement Student. The Athlete class does not implement the Student interface. Please note that interface is no longer a part of the AP CSA exam.
```
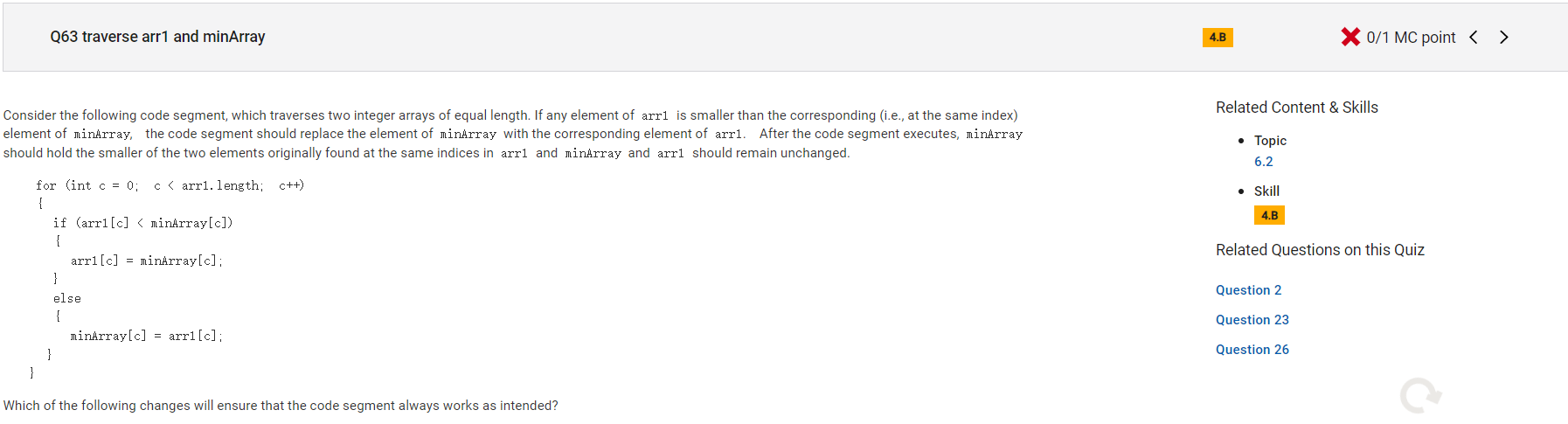
 ```
```
Answer E
Incorrect. The code segment is intended to leave arr1 unchanged and store the smaller of two values in minArray. If lines 7–10 are removed, the code segment will store the smaller of each pair of values in arr1.
Correct Answer: C
Reason: Line 5 modifies an element of arr1 if that element is smaller than the corresponding element of minArray, which is NOT what is intended, since arr1 should remain unchanged.
```
Collegeboard 52 Qs
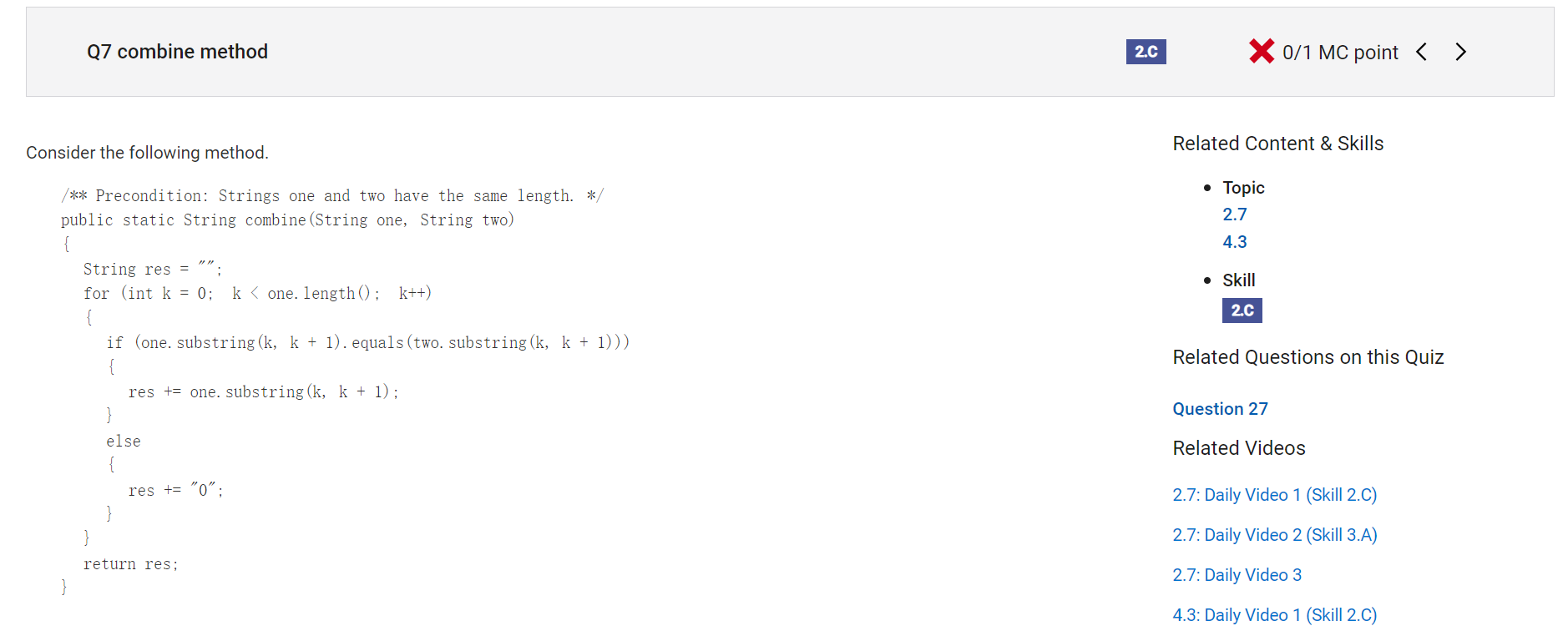
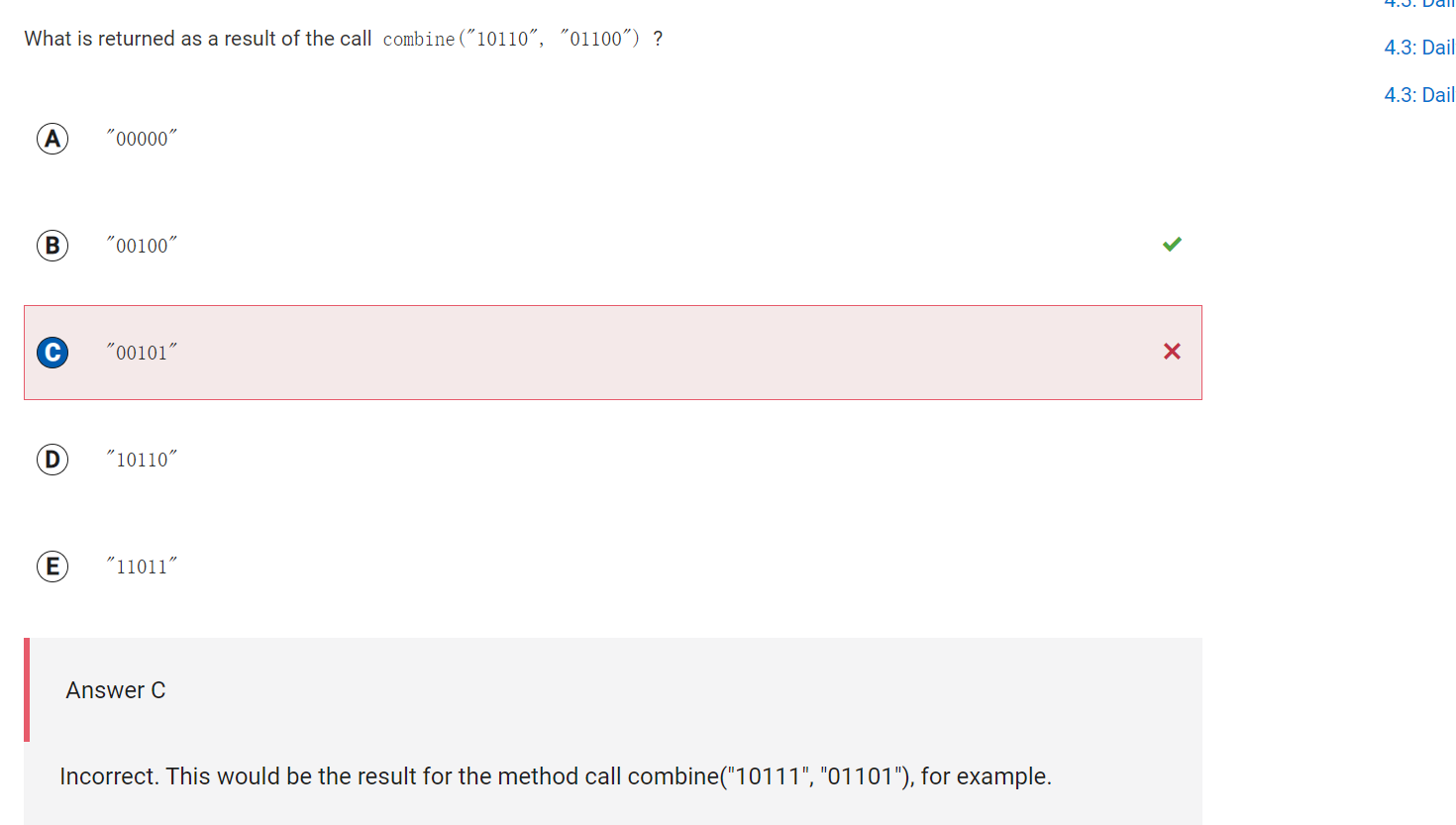 ```
</h2>
Answer C
```
</h2>
Answer CIncorrect. This would be the result for the method call combine("10111", "01101"), for example.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: The combine method compares corresponding substrings of length 1 from input strings one and two. If the substrings are the same, the substring is appended to res; otherwise, "0" is appended to res. The first and second characters of res are "0" because the characters in position 0 and the characters in position 1 of one and two differ. The third character of res is "1" because the characters in position 2 of one and two are both "1". The fourth character in res is "0" because the characters in position 3 of one and two differ. The fifth character in res is "0" because the last characters of one and two are both "0". The value "00100" is returned. </h2> ```
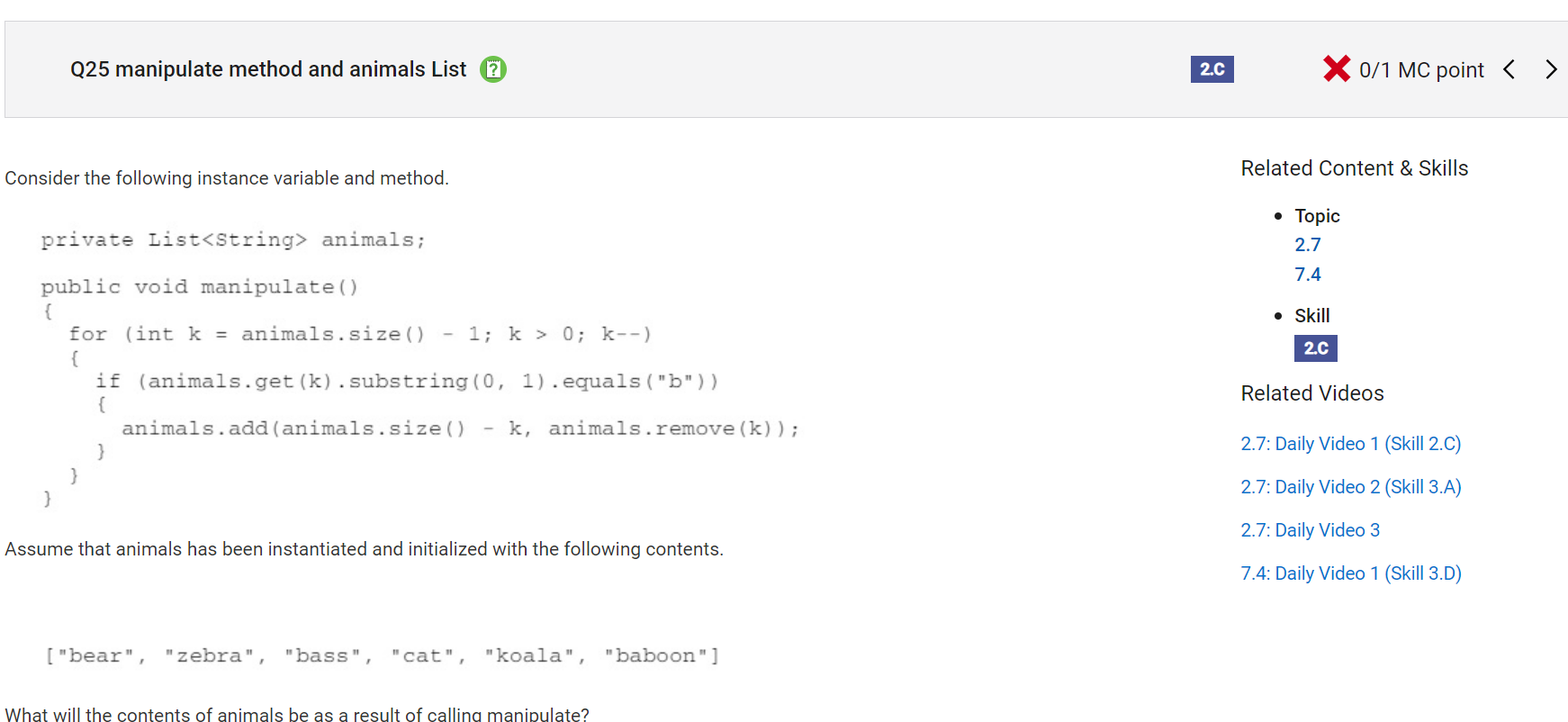
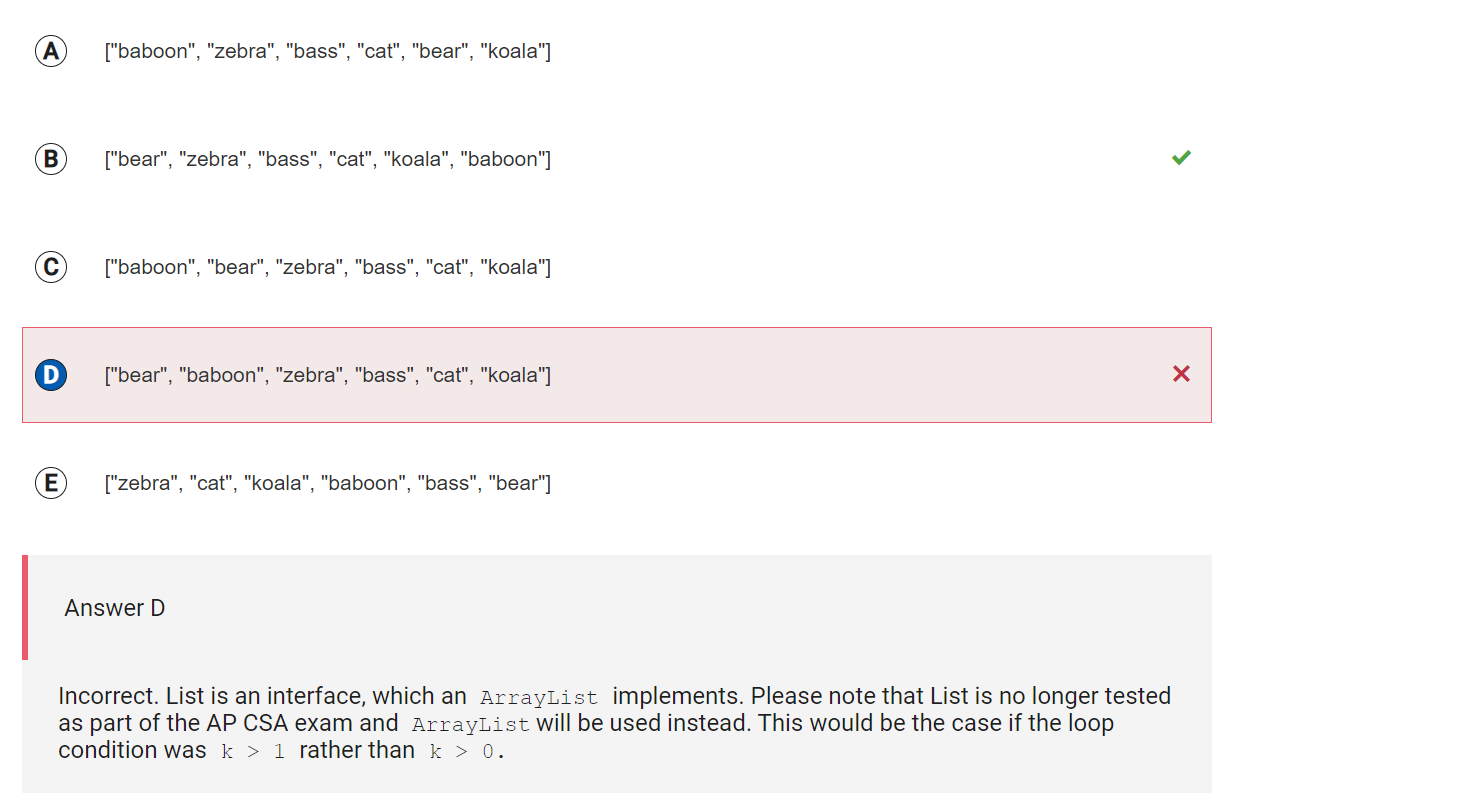 ```
```
Answer D
Incorrect. List is an interface, which an ArrayList implements. Please note that List is no longer tested as part of the AP CSA exam and ArrayList will be used instead. This would be the case if the loop condition was k > 1 rather than k > 0.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: List is an interface, which an ArrayList implements. Please note that List is no longer tested as part of the AP CSA exam and ArrayList will be used instead. The manipulate method contains a for loop with a loop control variable k that starts at the right most index of animals, decrements by 1 each time, until k is equal to 0. In the first iteration, when k is 5, if the element of animals at 5 (“baboon”) starts with a “b”, which it does, then this value is removed from the list and inserted at index 1. The list would then be {“bear”, “baboon”, “zebra”, “bass”, “cat”, “koala”}. In the second iteration, when k is 4, the element of animals at 4 (“cat”) does not start with a “b” and no changes are made to the list. In the third iteration, when k is 3, the element of animals at 3 (“bass”) starts with a “b”. This value is removed from the list and inserted at index 3. Since it was already at index 3, the list would not change. In the fourth iteration, when k is 2, the element of animals at 2 (“zebra”) does not start with a “b” and no changes are made to the list. In the fifth iteration, when k is 1, the element of animals at 1 (“baboon”) starts with a “b”. It is removed from the list and inserted at index 5. The list would then be {“bear”, “zebra”, “bass”, “cat”, “koala”, “baboon”}. Finally, k decrements to 0 which is not greater than 0 so the loop terminates.
```
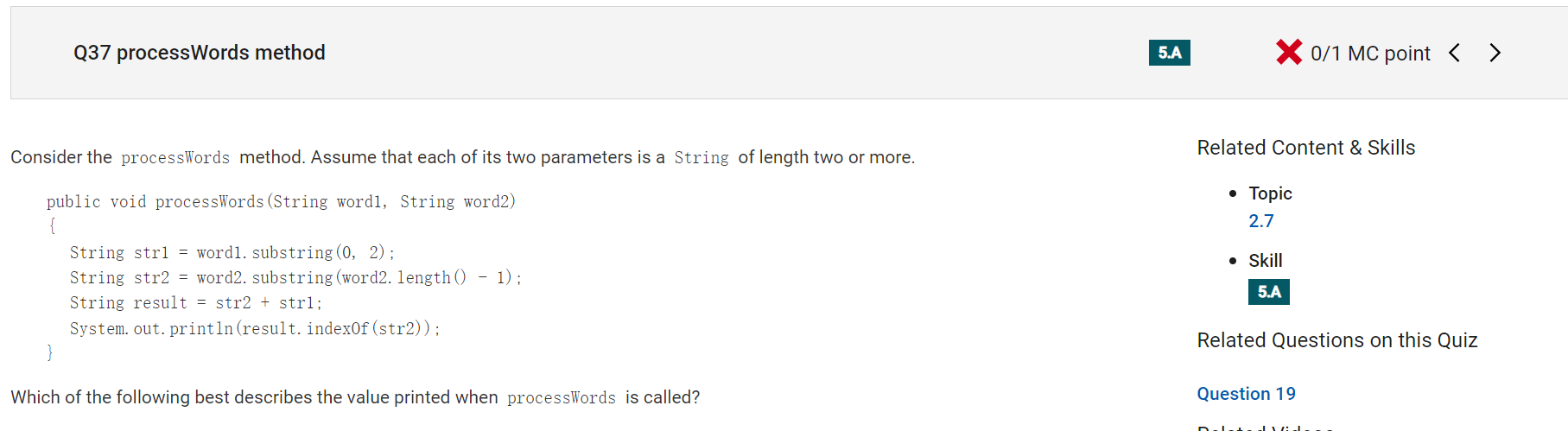
 ```
```
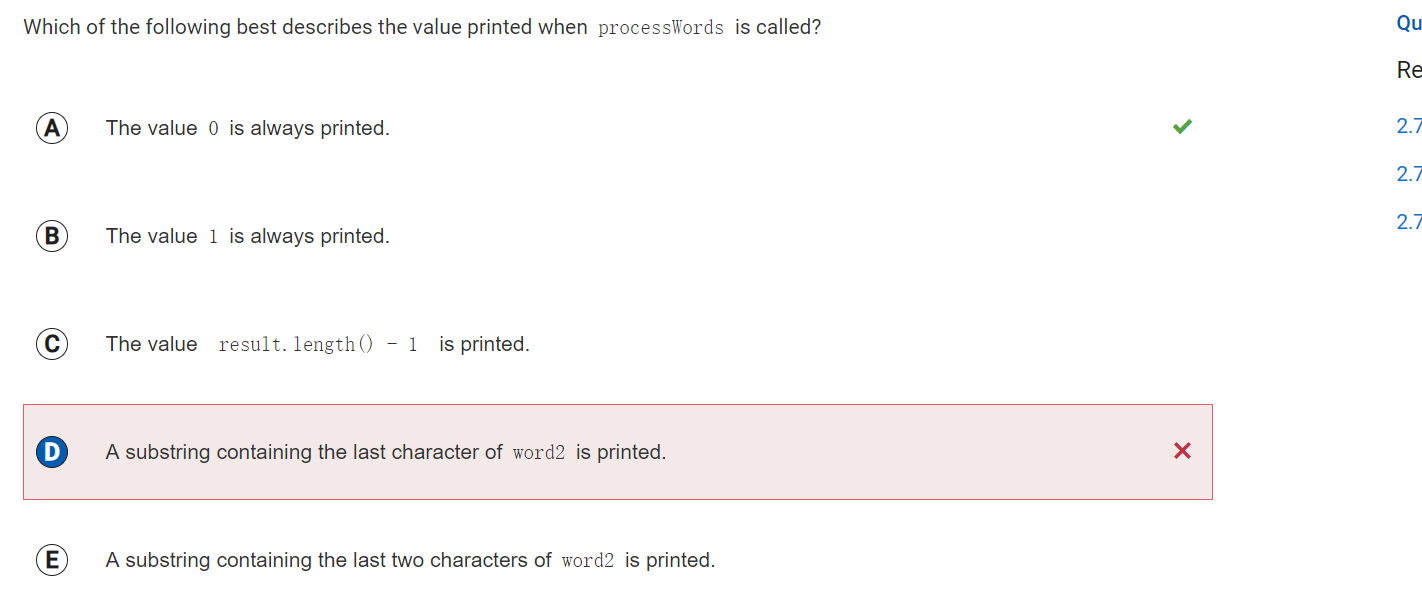
Answer D
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: A
Reason: System.out.println(result.indexOf(str2)); is what it call. So it will print the index of str2 which is always 0.
```
 ```
```
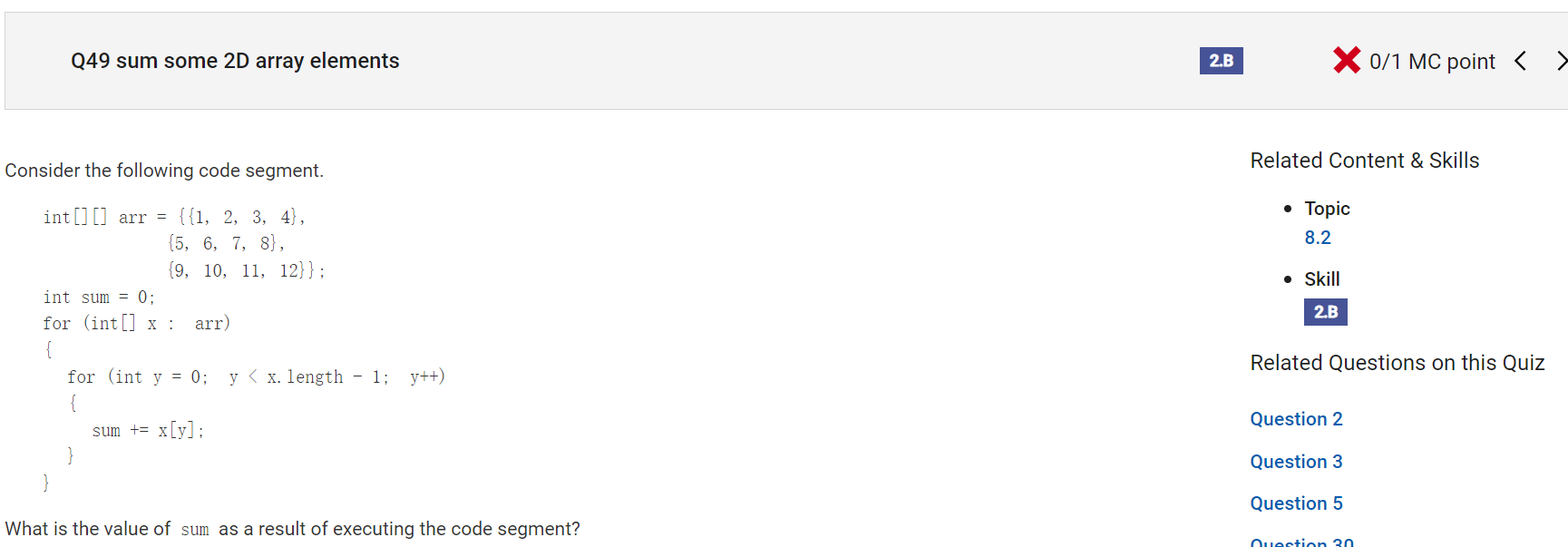
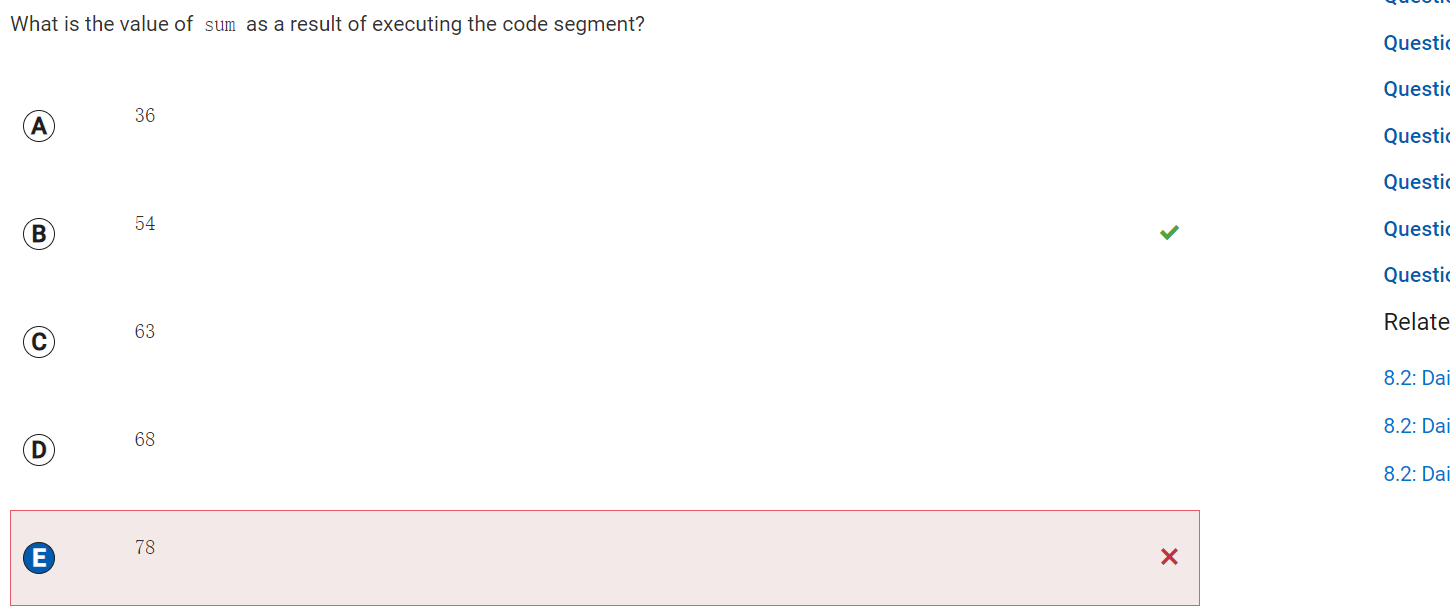
Answer E
Incorrect.
Correct Answer: B
Reason: y < x.length - 1; not y < x.length[0] - 1; So it will not goes through all the columns in each row.
```
2015 Practice Exam MCQ
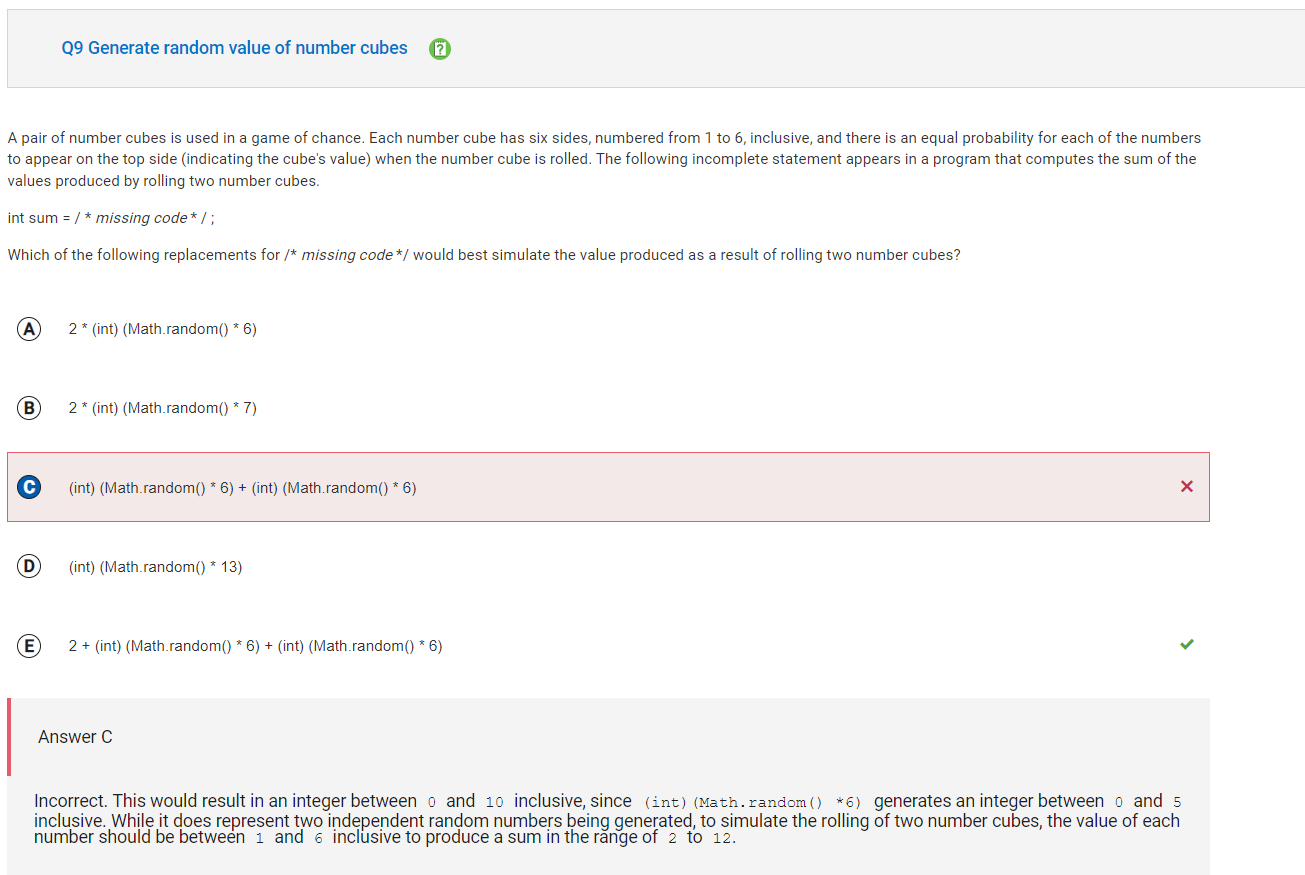 ```
```
Answer C
Incorrect. This would result in an integer between 0 and 10 inclusive, since (int)(Math.random() *6) generates an integer between 0 and 5 inclusive. While it does represent two independent random numbers being generated, to simulate the rolling of two number cubes, the value of each number should be between 1 and 6 inclusive to produce a sum in the range of 2 to 12.
Correct Answer: E
Reason: The call Math.random() will produce a double between 0 and 1, not including 1. To generate a random number in the range of 1 to 6, the call Math.random() needs to be multiplied by the number of integers you want to generate, in this case 6, giving us Math.random() * 6. This will result in a double between 0 and 6, not including 6. If we type cast this to an int, as in (int)(Math.random() * 6), the result will be an integer between 0 and 5 inclusive. Adding 1 will adjust the range to 1 to 6 inclusive, as in (int)(Math.random() * 6) + 1. This expression will simulate the rolling of one number cube. Since each roll is independent, to simulate rolling two number cubes, we need to use this expression twice which simplifies to 2 + (int)(Math.random() * 6) + (int)(Math.random() * 6).
```
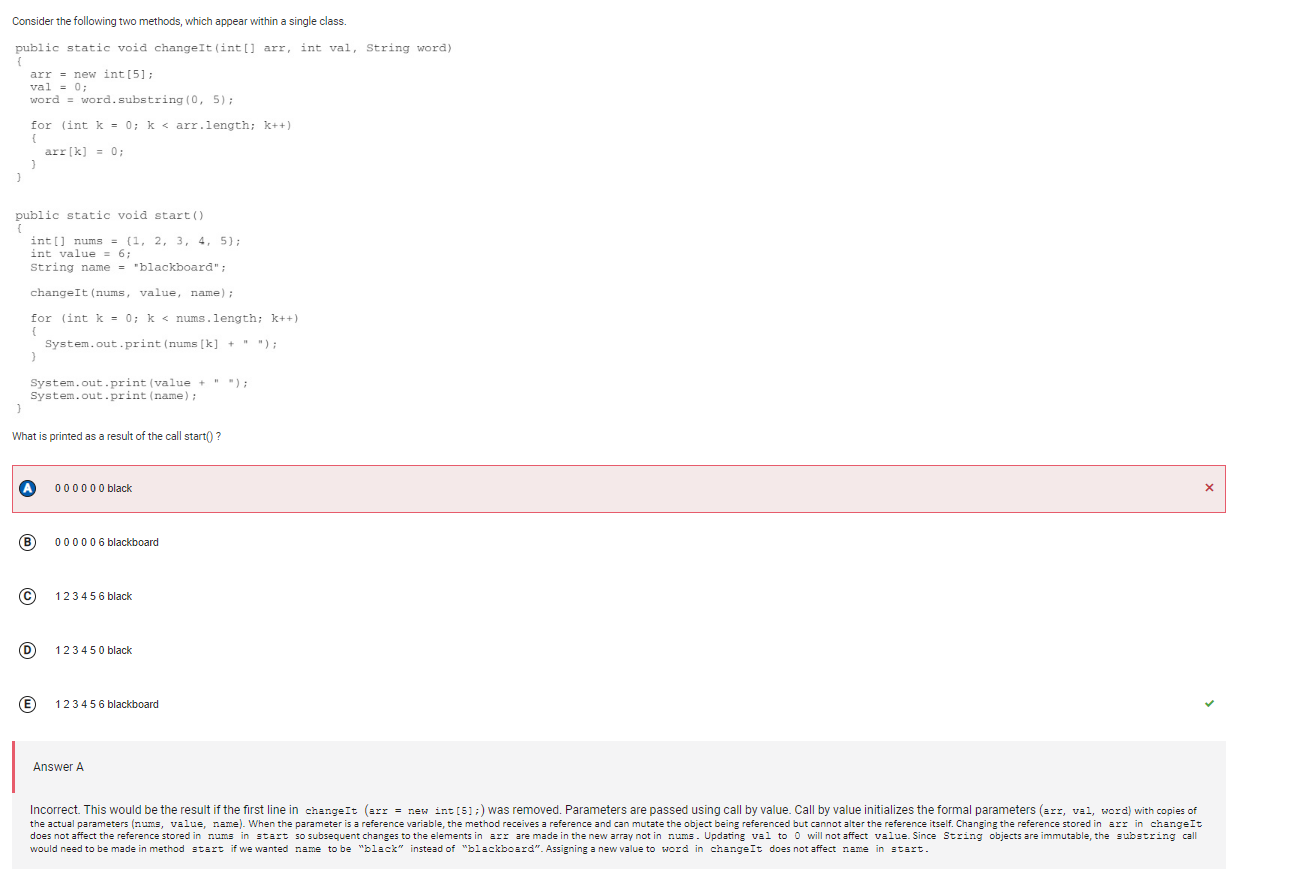 ```
```
Answer A
Incorrect. This would be the result if the first line in changeIt (arr = new int[5];) was removed. Parameters are passed using call by value. Call by value initializes the formal parameters (arr, val, word) with copies of the actual parameters (nums, value, name). When the parameter is a reference variable, the method receives a reference and can mutate the object being referenced but cannot alter the reference itself. Changing the reference stored in arr in changeIt does not affect the reference stored in nums in start so subsequent changes to the elements in arr are made in the new array not in nums. Updating val to 0 will not affect value. Since String objects are immutable, the substring call would need to be made in method start if we wanted name to be “black” instead of “blackboard”. Assigning a new value to word in changeIt does not affect name in start.
Correct Answer: E
Reason: Parameters are passed using call by value. Call by value initializes the formal parameters (arr, val, word) with copies of the actual parameters (nums, value, name). When the parameter is a reference variable, the method receives a reference and can mutate the object being referenced but cannot alter the reference itself. Passing an object reference as a parameter will result in the formal parameter and the actual parameter being aliases. They both refer to the same object. When we call changeIt and pass the objects num and name, the formal parameters arr and word will reference these same objects. A copy of the object is not made. However, the first part of the method assigns new objects to arr and word, which means that any changes made to arr and word do not affect the actual parameters num and name. They remain unchanged. Updating val to 0 will not affect value. Therefore, the original values for num, value and name are printed.
```
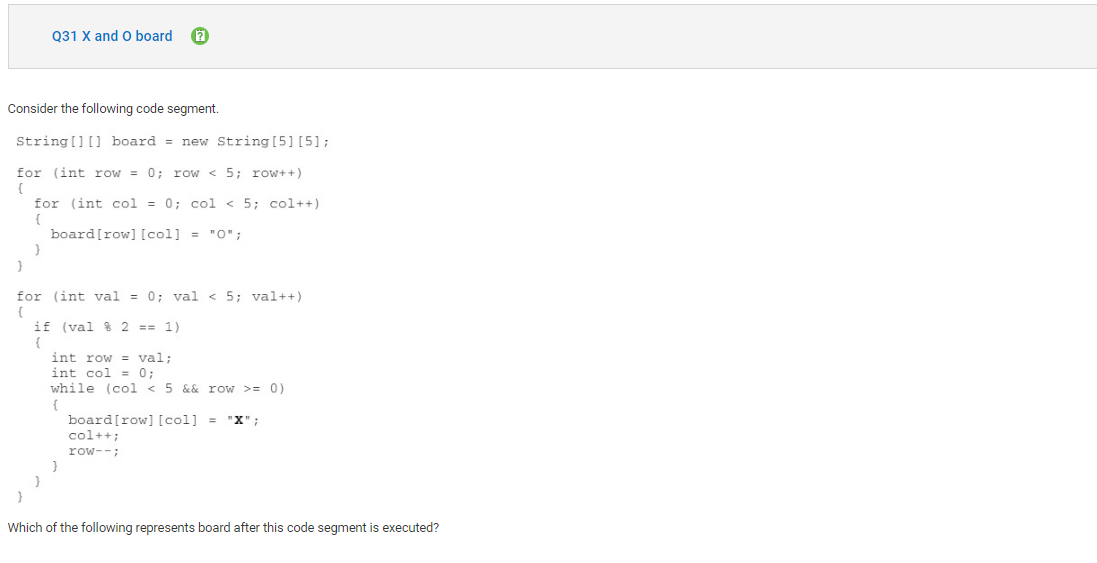
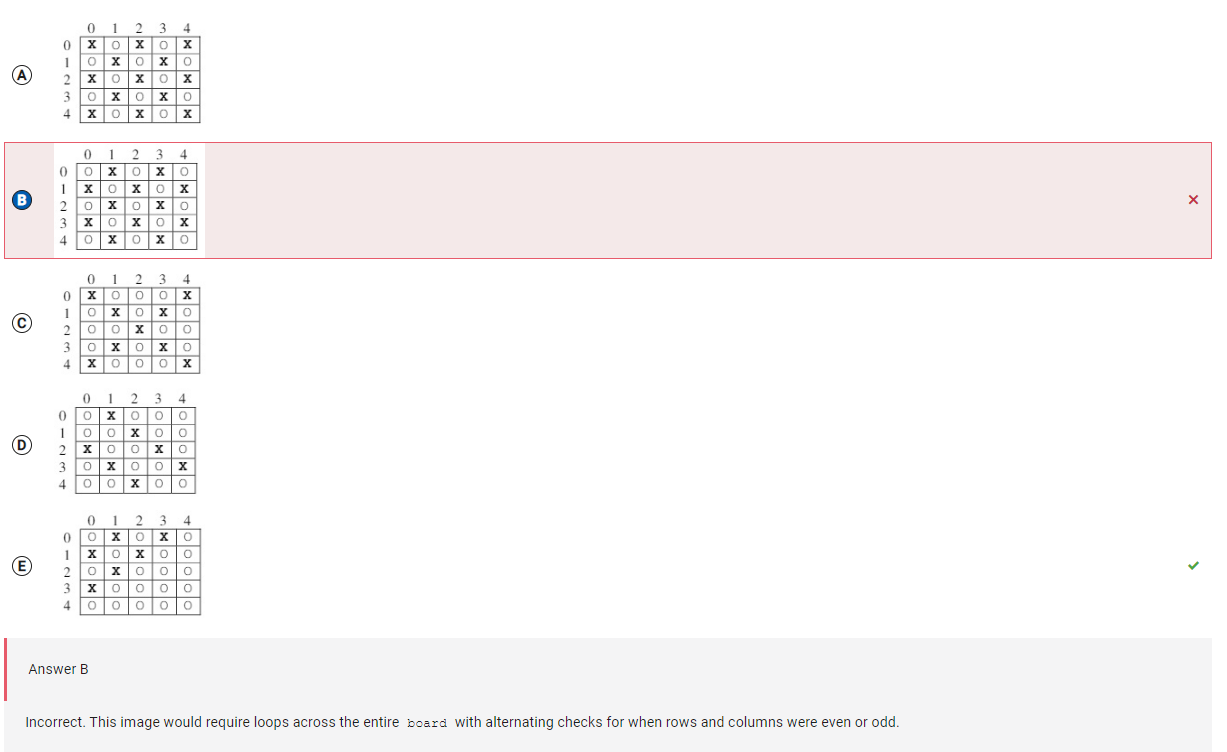 ```
```
Answer B
Incorrect. This image would require loops across the entire board with alternating checks for when rows and columns were even or odd.
Correct Answer: E
Reason: The first set of nested for loops sets each element in board to “O”. The next for loop starts val at 0 and increments by 1 until val is 4, when val is 5 the loop terminates. When val is even, board is not updated, so nothing happens when val is 0. When val is 1, row is assigned 1 and col is assigned 0. The boolean condition in the while loop is true, so board[1][0] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 1 and row is decremented to 0 and board[0][1] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 2 and row is decremented to -1 and the while loop terminates. When val is 2, nothing changes about board. When val is 3, row is assigned 3 and col is assigned 0. The boolean condition in the while loop is true, so board[3][0] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 1 and row is decremented to 2 and board[2][1] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 2 and row is decremented to 1 and board[1][2] is assigned “X”. Then col is incremented to 3 and row is decremented to 0 and board[0][3] is assigned “X”. Finally, col is incremented to 4 and row is decremented to -1 and the while loop terminates. When val is 4, nothing changes about board.
```
 ```
```
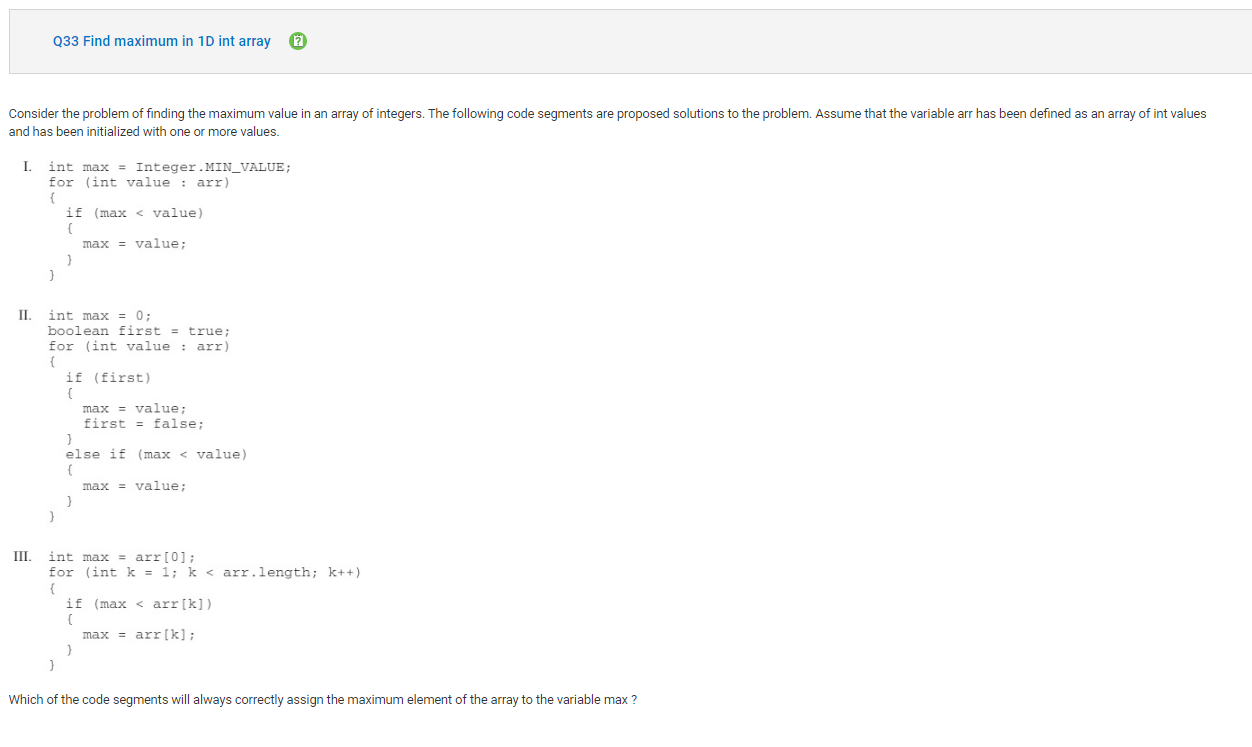
Answer C
Incorrect. Choice I sets max to Integer.MIN_VALUE, which is the smallest possible integer value. Then it accesses each element in arr and assigns them value. If value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far. Choice II uses an if statement inside the for loop to check and see if value is the first element in arr or not. Once the first element is identified, max is initialized to the first element and first is set to false. For all subsequent elements in arr, if value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far.
Correct Answer: E
Reason: Choice I sets max to Integer.MIN_VALUE, which is the smallest possible integer value. Then it accesses each element in arr and assigns them value. If value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far. Choice II uses an if statement inside the for loop to check and see if value is the first element in arr or not. Once the first element is identified, max is initialized to the first element and first is set to false. For all subsequent elements in arr, if value is greater than max, max is assigned value since it is now the largest value so far. Choice III sets max to the first value in arr. Then it accesses each subsequent value in arr checking to see if the value is greater than max, if it is max is assigned this element since it is now the largest value so far.
```
 ```
```