Fastpages Java Notebook Blog Post
First try of creating a Java Jupyter notebook
- Week 2 Gui Menu
- Iteration with 2D Array
- Class running Fibonacci
- Original Class (The class that I will use to extends for, keep not change)
- For loop Example
- Fetch and Backed RapidAPI. (Pair/Individual)
- Java RapidAPI
- Arrays and Images
- Hacks
- List and ArrayLists (Pair)
- POJO and @Entity Definition
- Homework: 2006 Collegeboard FRQ parts 2a and 3a. Part 1 is optional.
- 2019 FRQ1 HW
- Period 1 Iteration HW
- Period 1 Using Objects HW
- Unit 05 Thu - Writing Classes HW
- FRQ2 APCalendar
- Unit 07 - ArrayList HW
- 2019 FRQ 4 Lightboard
- Unit 9 HW Part1 and Part2
- Unit 6 Array HW
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
HelloWorld.main(null);
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
HelloWorld.main(null);
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
// Graphical-User-Interface for Desktop in Java using Java Swing.
public class MenuJFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private JFrame frame;
private JMenuBar menubar;
private JMenu menu;
private JLabel message = new JLabel("Click on Menu to select an action.");
public final String[] MENUS = { // 1D Array of Menu Choices
"Home", "Game1", "Creators' interests", "Loading bar",
};
// Statics to assist with timer and messaging, single copy (no instance)
private static int delay = 20;
private static int step = 1;
private static String hashes = "";
// Constructor enables the Frame instance, the object "this.frame"
public MenuJFrame(String title) {
// Initializing Key Objects
frame = new JFrame(title);
menubar = new JMenuBar();
menu = new JMenu("Menu");
// Initializing Menu objects and adding actions
for (String mx : MENUS) {
JMenuItem m = new JMenuItem(mx);
m.addActionListener(this);
menu.add(m);
}
// Adding / Connecting Objects
menubar.add(menu);
frame.setJMenuBar(menubar);
frame.add(message);
// Sets JFrame close operation to Class variable JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// set the size of window based on objects
frame.setSize(600,400);
// makes the frame object visible according to properties previously set
frame.setVisible(true); // flow of control shifts to frame object
}
// event from user selecting a menu option
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// local variable to ActinEvent
String selection = e.getActionCommand(); // menu selection
String msg; // local variable to create response from action
final String[] COLORS = {"Red", "Green", "Blue"}; // add more colors here
final String start_msg = "<html>"; // html building
final String end_msg = "</html>";
final String hash = "#";
int highestGrade = 0;
int lowestGrade = 0;
int grade1 = 50;
int grade2 = 100;
// run code based on the menuItem that was selected
if ( selection.equals(MENUS[0]) ) { // Hello Action
msg = "Mini Online Games center";
message.setText(msg);
} else if ( selection.equals(MENUS[1]) ) { // Color Action
highestGrade = Math.max(grade1, grade2);
lowestGrade = Math.min(grade1, grade2);
message.setText(
"<html>Let start with a warm up math game about how to calculate your average Grade<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"First we have two grades: " + grade1 + " and " + grade2 + "<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"Then find the highest Grade, using highestGrade = Math.max(grade1, grade2);" + "<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"Now we find the highest Grade: " + highestGrade + "<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"Then find the lowest Grade, using lowestGrade = Math.min(grade1, grade2);" + "<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"Now we find the lowest Grade: " + lowestGrade + "<br>"
+ "<br>" +
"Last, average the two value, we get our average grade: " + (highestGrade - lowestGrade) +
"</html>"
);
} else if ( selection.equals(MENUS[2]) ) {
msg = "My interest: play video games and my pair's interest: dog training";
message.setText(msg);
} else { // Loading Bar Action
String loading = "<p>Loading</p>";
// Code to run on a Timer
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
public void run() { // Method for TimerTask
// Static and Local variables used to manage message building
int random = (int) (Math.random() * COLORS.length); // random logic
MenuJFrame.hashes += "<font color=" + COLORS[random] + ">" + hash + "</font>";
String msg = start_msg + loading + hashes + end_msg;
message.setText(msg);
// Shutdown timer and reset data
if(MenuJFrame.step++ > MenuJFrame.delay) {
MenuJFrame.step = 1; MenuJFrame.hashes="";
timer.cancel();
}
};
};
// Schedule task and interval
timer.schedule(task, 200, 200);
message.setText(start_msg + loading + hash + end_msg); // prime/initial display
}
}
// Driver turn over control the GUI
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Activates an instance of MenuJFrame class, which makes a JFrame object
new MenuJFrame("Menu");
}
}
MenuJFrame.main(null);
class MonkeyLoop {
//The area between class definition and the 1st method is where we keep data for object in Java
String [][] monkeys; //2D Array: AP CSA Unit 8: 2D array of strings
String [][] cthulhus; //2D array is like a grid [x][y]
// or like a spreadsheet [row][column]
/**
* Constructor initializes a 2D array of Monkeys
*/
public MonkeyLoop() {
//Storing Data in 2D arrays
monkeys = new String[][]{ //2D array above is just a name, "new" makes a container ("object")
//Monkey 0
{
"ʕง ͠° ͟ل͜ ͡°)ʔ ", //[0][0] eyes
" \\_⏄_/ ", //[0][1] chin
" --0-- ", //[0][2] body
" ⎛ ⎞ " //[0][3] legs
},
//Monkey 1
{
" ʕ༼ ◕_◕ ༽ʔ", //[1][0]
" \\_⎏_/ ",
" ++1++ ",
" ⌋ ⌊ "
},
//Monkey 2
{
" ʕ(▀ ⍡ ▀)ʔ", //[2][0]
" \\_⎐_/ ",
" <-2-> ",
" 〈 〉 "
},
//Monkey 3
{
"ʕ ͡° ͜ʖ ° ͡ʔ", //[3][0]
" \\_⍾_/ ",
" ==3== ",
" _/ \\_ "
},
//Monkey 4
{
" (◕‿◕✿) ", //[4][0]
" \\_⍾_/ ", //[4][1]
" ==4== ", //[4][2]
" _/ \\_ " //[4][3]
},
};
cthulhus = new String[][]{
{
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡠⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢎⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ʕง ͠° ͟ل͜ ͡°)ʔ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠂⢱⠀⠀⢀⣤⡀⠀⠀⢣⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ \\_⏄_/ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣰⠻⠉⣧⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⢸⠇⠀⠐⠉⡆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ --0-- ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⠔⠒⢦⠀⢻⡄⠀⢿⣻⣿⡿⢀⣴⣋⣄⣄⣌⣠⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ⎛ ⎞ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠀⢀⡞⠀⠈⠛⣷⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣯⣥⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠷⣦⣴⡾⢿⣿⡿⢿⣿⣋⣽⠶⢦⠙⢷⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣾⡏⢀⡆⠈⠉⠁⡄⠈⡇⠘⢇⠀⢈⡆⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⡯⠀⠸⠁⠀⠀⠸⣧⡀⡇⠀⠈⠉⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠸⣇⡴⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠙⠛⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ "
},
{
" ʕ༼ ◕_◕ ༽ʔ ",
" \\_⎏_/ ",
" ++1++ ",
" ⌋ ⌊ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡤⠊⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣠⡎⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣾⡟⠀⠙⣆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣟⡇⠀⠀⠈⣇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⡧⣅⠀⠀⠐⣽⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣗⠢⠀⠀⠀⠹⣿⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⠑⠂⠀⠀⠸⢿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⡴⠶⠶⠲⢶⣦⣄⠀⠀⠀⠀⢻⣤⠃⠄⠀⠴⢺⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡟⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠙⢿⠷⣄⠀⠀⢸⡦⠚⣁⡀⢈⣹⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠻⣿⣇⠀⠀⣷⡖⢐⢩⡡⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠨⡟⣿⡆⠀⢸⡧⠄⡄⢰⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢨⠆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡷⣳⡅⠀⠀⣷⠠⠩⠁⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⣀⣀⡤⠤⠒⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡄⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢨⡟⣦⡆⠀⠀⣾⣧⠄⠂⣁⡀⠀⠀⠀⣠⡶⠞⠛⠉⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠣⢀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣠⣮⢲⣿⠇⠀⠰⣼⣿⠀⡀⣀⠀⡀⠀⣼⣷⠇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠙⠒⢶⣆⢾⢿⣭⡿⠃⠀⠠⠤⠊⢽⡗⡴⢀⠁⠃⠀⣿⡼⢀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣀⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⢴⣛⣿⣿⡿⢿⣳⡄⠠⠤⠬⠈⣿⣷⠄⠄⡈⠘⠣⠹⣿⣷⣄⢠⣴⣚⠟⠛⠉⠙⠳⣆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣄⠀⠀⠀⠀⣆⠋⠯⡷⣾⠟⠀⠀⡃⣯⠀⠠⠐⢋⡟⢿⡁⢁⠀⢂⢔⣆⠈⢻⣿⠖⢨⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⣧⠀⢠⡋⣉⠤⠬⣽⡏⠀⠀⣢⣭⣀⡉⠄⠳⢺⡇⢸⠫⠑⠀⠄⣀⣈⣄⠾⣟⠿⡖⢘⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⢀⡖⠛⠂⣰⣦⣿⢀⡀⣿⣿⠛⠁⠀⠈⢒⣿⠁⢸⠗⠒⠂⢄⠁⠀⢻⣏⣮⠀⠙⣦⡄⠀⠉⠀⠀⢠⠎⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡟⢸⡷⢾⠑⢥⣨⣿⢃⣬⠞⡿⠀⠄⠁⢀⢠⡟⠀⢸⡤⠈⠠⠀⠑⡀⠹⣷⣿⡄⠀⣷⡤⠀⠈⠘⡀⡞⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⠃⣿⣬⢴⠻⣁⣛⣿⡼⠁⢰⢤⣤⠘⠀⠁⢋⡇⠀⣾⡁⠀⢀⠀⡦⢤⢴⣿⣽⣷⢀⣿⠤⠀⠈⠉⠃⣧⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡚⠀⣿⣀⣀⡕⢧⣨⣭⣇⠀⣄⠀⡀⠔⠌⠋⠙⡇⢰⣿⠙⠋⠃⠈⡀⠀⢀⠉⣿⣻⣿⡧⠀⠀⠈⠈⠁⢸⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⡀⠀⠇⠀⢸⣈⠐⢀⡔⠥⣤⣽⣶⠃⠩⠁⠀⠐⠀⢲⣧⣾⠗⠄⠂⠀⠀⠈⠙⠸⠀⣿⣽⡯⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠃⠀⢇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠂⠀⠰⡄⠀⣿⡿⠈⠈⣰⠂⠤⢼⠆⠒⠒⡀⠄⢀⣨⣿⣁⢀⣀⠀⠈⠢⠤⢀⡆⢠⣿⠯⢀⡀⠀⠀⠄⠘⠀⠀⢸⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠂⢼⣿⡟⡞⠉⠍⠐⠸⡄⠀⠀⠄⠈⣩⡟⠉⠡⠈⠀⢀⡀⠀⢀⣠⢃⠾⠍⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠁⠃⠀⠀⡈⠀⢐⠀⠀⠀"
},
//Cthulhu 2
{
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⣤⣶⣷⣾⣿⣾⣶⣤⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣠⣤⣤⣄⣄⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⡄⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣠⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣶⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣰⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣴",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣰⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⠛⠿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢰⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⠁⠀⢀⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠋⠀⠀⢀⣠⣰⣾⣾⣿",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⣼⣿⣿⠏⡿⠋⠀⠀⠉⢿⡆⠀⠈⠻⣿⣯⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣾⣿⣿⣿⣏⠀⠀⣠⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⠋⢀⣴⣬⣿⣿⡿⡛⢿⣷",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⠃⠀⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⣸⣿⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⣦⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⢀⣾⣿⣿⣿⣾⠟⣣⣴⠋⢻⣿⣏⣉⣿⣿⣿⣿",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠈⣿⣿⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣰⡿⠃⠀⠀⠀⣿⣥⣟⡝⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⢻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣼⣿⣿⣾⡟⢻⣿⡿⡟⠿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠘⠿⣿⣶⣶⣶⣶⠿⠛⠁⠀⠀⠀⣴⡿⣷⣿⣥⣴⣶⣶⣶⣤⣤⣀⣿⣿⣿⣿⣫⣿⣿⣿⡿⢛⣿⣿⠛⠟⠈⢠⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿",
" ʕ(▀ ⍡ ▀)ʔ ⠀⠀⣀⡤⠤⣄⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⢷⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣩⣿⡿⢿⣉⣽⣿⢟⠟⠉⠀⢠⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿", //[2][0]
" \\_⎐_/ ⠀⣼⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣴⣿⣟⣿⣿⣿⣿⢿⠾⠿⠿⢿⢿⣦⣿⣿⣿⡿⠻⣯⣼⣿⣿⡛⠁⠀⢀⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿ ",
" <-2-> ⣸⡟⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣴⣿⣿⣿⣟⣿⣿⣿⣅⡀⠀⣀⣀⣤⣴⡿⣿⠛⣻⣷⡾⠿⣯⡸⢿⣿⣦⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿ ",
" 〈 〉 ⢿⣿⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣠⣾⣿⣿⣿⢼⣿⣯⣿⣛⣿⣿⠿⣿⣛⣿⣷⣼⣿⣿⠟⣻⡳⢖⠛⢿⣿⣟⠛⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⣿ ",
" ⠘⣿⣿⣦⣤⣤⣀⣠⣤⣴⣿⡿⣿⡿⠟⠁⠀⠙⠿⢿⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⣿⡯⠅⠉⠀⠙⢿⣿⣿⣿⡛⠿⣿⣿⣷⣦⣿⣿⣷⣿⣿⣿⣿",
" ⠀⠘⠻⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠿⠟⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠁⠈⠁⠈⠉⣽⣿⠋⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⡤⠶⠻⠿⠛⠻⠛⠿⠛⠿⠛⠛⠛⠋⠉⠉⠁",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠁⠁⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠘⢿⣿⣄⣀⣀⣤⠾⠋⠀⠀⠀⠐⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠛⠋⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀"
},
//Cthulhu 3
{
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣼⡏⠀⠀⠀ʕ ͡° ͜ʖ ° ͡ʔ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢿⣧⠀⠀⠀⠀\\_⍾_/ ",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⢻⣷⡀⠀⠀⠀==3==⠀⠀⠀⠈⠢⣄⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠹⣿⡄ _/ \\_ ⠉⠙⠻⣷⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢹⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣄⣮⠟⠀⠀",
" ⠀⢀⣠⣲⣶⠶⣄⠀⠀⣸⠯⠂⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢯⠟⠇⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⡞⣾⡟⢻⣍⣼⠇⣰⣿⡿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣶⠦⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠩⢪⢄⠀⠀",
" ⢸⢮⡭⡇⠀⠙⢉⣼⡿⣾⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠁⠵⣦⡉⠈⠀⠀⢀⢪⡫⡄⠀",
" ⠘⣸⣮⣷⡀⠀⣸⣿⣿⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠐⣭⣆⠀⠀⡐⠗⡭⠢⠀",
" ⠀⠘⡽⡫⣿⡄⢿⣿⣷⣱⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣠⢖⢝⣳⠞⣠⣼⣏⢏⣧⠛⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠰⣉⣟⣿⡘⣿⣿⣿⢵⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣟⡏⠀⠀⣾⣿⣿⡇⣠⡑⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠈⠉⠉⠁⠘⠉⠛⠈⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠋⠀⠀⠉⠉⠉⠁⠉⠀⠀⠀"
},
//Cthulhu 4
{
" (◕‿◕✿) ", //[4][0]
" \\_⍾_/ ", //[4][1]
" ==4== ", //[4][2]
" _/ \\_ ",
" ",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣴⣆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢺⣿⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣾⣿⣷⣦⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣹⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣴⣤⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠸⣇⠀⠈⢿⣿⡆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣼⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠸⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⡏⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⢠⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣾⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣸⣿⣿⠃⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣷⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠠⣶⣾⣷⣦⣤⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠘⣿⣿⣷⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠘⣿⡀⠈⠻⣿⣿⣆⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢿⣿⣿⣄⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠈⠁⠀⠀⠈⢿⣿⣷⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣷⠀⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⡿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⣀⣀⢀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⣿⣿⣷⡄⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⣿⣿⣿⡦⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣽⣿⣿⠇⠀⠀⠀⠀⢠⣾⣿⡿⠿⠿⠿⣿⣦⡀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠹⣿⣿⣧⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⢰⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⣰⣿⣿⠏⠀⠀⠀⠸⠾⠿⠃",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠹⣿⣿⣿⣆⡀⠀⠀⠘⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⢀⣾⣿⣿⡏⠀⠀⠀⠀⣻⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠙⣿⣿⣿⣷⡄⠀⠀⣿⣿⣿⡟⢰⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⣼⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣻⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⢿⣿⣿⣿⣆⠀⢹⣿⣿⣇⢸⣿⣿⣿⡇⠀⢀⣼⣿⣿⣿⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠻⣿⣿⣿⣧⢸⣿⣿⣿⣸⣿⣿⣿⠀⢠⣾⣿⣿⣿⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣼⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠹⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠃⠀⢀⣠⣴⣾⣿⣿⣿⠟⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠙⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣵⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠛⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠟⠋⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⠋⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠇⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠏⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠏⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀",
" ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣏⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀"
},
};
}
/**
* Loop and print monkeys in array
* ... repeat until you reach zero ...
*/
public void printPoem() {
//begin the poem
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Monkey Jumpers Poem in Java Loopy");
System.out.println("One day, there are total of five little monkeys want to jump on the bed to sleep");
// monkeys (non-primitive) defined in constructor knows its length
int monkeyCount = monkeys.length;
int Crow = 4;
int row1 = 4;
int Crow2 = 1;
int Ccol2 = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < monkeyCount; row++) { //cycles through "cells" of 2d array
/*cycles through columns to print
each monkey part by part, will eventually print entire column*/
for (int col = 0; col < monkeys[row].length; col++) {
// prints specific part of the monkey from the column
System.out.print(monkeys[row][col] + " ");
//this is new line between separate parts
System.out.println();
}
//this new line gives separation between stanza of poem
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = monkeyCount; i >= 1; i--) //loops through 2D array length backwards
{
//how many separate parts are there in a monkey monkey?
System.out.println("000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000");
System.out.println("They line up and goes one by one");
System.out.println("000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000");
for (int row = 0; row < monkeys[row].length; row++) { //cycles through "cells" of 2d array
/*cycles through columns to print
each monkey part by part, will eventually print entire column*/
for (int col = 0; col <= (monkeyCount - 1); col++) {
// prints specific part of the monkey from the column
System.out.print(monkeys[col][row] + " ");
//this is new line between separate parts
}
//this new line gives separation between stanza of poem
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Look, one little monkeys jumping on the bed");
for (int col1 = 0; col1 < monkeys[row1].length; col1++) {
System.out.print(monkeys[row1][col1] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
row1 -= 1;
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("jumping to the the arms of Cthulhu");
System.out.println();
for (int Ccol = 0; Ccol < cthulhus[Crow].length; Ccol++) {
// prints specific part of the monkey from the column
System.out.print(cthulhus[Crow][Ccol] + " ");
//this is new line between separate parts
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Now, there are " + (i-1) + " little monkeys left");
//countdown for poem, decrementing monkeyCount variable by 1
monkeyCount -= 1;
Crow -= 1;
}
//out of all the loops, prints finishing messages
System.out.println("No more monkeys jumping on the bed");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
for (int Crow1 = 3; Crow1 != -1; Crow1--) {
for (int Ccol1 = 0; Ccol1 != 5; Ccol1++) {
// prints specific part of the monkey from the column
System.out.print(monkeys[Ccol1][Crow1] + " ");
//this is new line between separate parts
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
System.out.println("0000000000000000000000000000000000");
System.out.println(" THE END ");
System.out.println("0000000000000000000000000000000000");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⢛⣛⣼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⠛⠛⠋⠛⠛⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠟⣡⣈⡈⢻⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⢰⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠋⠈⠀⣂⣐⡒⠀⠀⠀⠙⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣎⣚⣸⡃⢹⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣀⣍⡀⠑⠍⠻⣿⡏⠠⡀⢉⣉⠙⢻⣷⡄⠐⠀⠀⣻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡁⠘⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣦⡄⠀⠀⢀⠠⠹⣿⣿⣇⢈⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⣸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣧⠀⠈⠌⠉⠉⠛⠻⣿⣿⣿⣿⡀⠁⠀⠂⠉⠈⠉⠁⣰⠟⠁⠀⠀⢠⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣖⠀⠀⠀⠙⡻⣿⣿⡇⠀⠀⢔⣿⣷⡾⠋⠀⠀⠀⠀⣤⡟⠉⣠⡤⠙⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⠿⠙⠋⠙⠛⠛⠟⢻⣿⣿⣷⣄⠀⠀⠀⢜⣿⠃⠀⡀⠀⠿⠍⠀⠀⠀⣠⣶⣿⣿⣷⠜⢇⡀⣀⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠿⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠉⠸⠟⣿⣆⡀⠀⠀⠈⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢉⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡌⠀⠙⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠉⠀⠀⠀⣤⣶⣤⣌⠀⠀⠀⠀⠪⠀⠀⠛⢻⠀⠀⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡆⠀⠀⠈⠛⠿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠃⠀⢼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣇⠀⠀⠄⡤⠁⣽⣿⣿⣿⣄⠀⠘⣢⡀⠀⠀⠈⠡⠀⠀⢐⠈⠡⠀⠀⠁⠀⠤⠀⠠⠀⠀⢿⠉⠑⠀⠀⣸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣧⠄⠀⠀⠠⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠆⠀⢨⣿⡄⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡀⠠⠀⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⡀⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢈⣺⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣶⡀⠀⠀⠙⠿⠿⣿⡿⠋⠀⠀⣲⠿⠋⠀⠀⠉⠀⠠⠀⠊⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣠⢸⡁⠑⣀⠀⠀⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣤⡄⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡀⣾⣿⠀⠀⢠⡀⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣀⣤⣶⡿⣟⡅⣢⠀⠀⠀⣠⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣶⣶⣴⠒⠒⠿⣿⡇⠀⢀⣗⣶⣶⢦⠖⢴⣖⡛⠉⣰⣷⠿⢫⣾⣞⣿⣿⣾⣿⣿⣯⡅⣼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠉⠀⠀⣐⠀⠸⠹⠀⢸⣹⣿⢣⡏⣾⣿⣿⣡⣼⢟⡡⣴⣿⣿⣿⣮⡻⣿⣿⣿⡿⡟⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠇⠸⡄⠉⠀⡸⡐⠀⡿⠿⠾⢸⣇⠢⠶⠛⢋⣡⣯⢾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢘⢿⣿⣷⣶⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡥⣄⠈⠙⠋⠀⢠⠌⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⡴⣱⣿⣿⣏⠿⠟⢛⣛⣛⣋⣿⣷⣮⣝⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣁⣶⣿⣿⣷⣼⣞⢤⡞⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣴⡿⢱⣿⡿⣿⣿⣶⣍⡻⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣷⣌⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢟⡝⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⢋⣾⠺⠁⠀⠀⠀⣀⣴⣿⢟⣱⣿⣿⣿⣷⣯⣽⢟⣴⣿⣿⡿⢋⣽⠟⣫⣽⣿⣼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⣷⠟⣼⣿⣿⣼⣿⢃⣿⡇⠀⠀⠀⣠⣾⣿⣿⢯⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢳⣿⣿⣿⠇⣰⣿⣣⣾⣿⣿⣿⡗⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⢇⡟⣴⣿⣿⣿⣿⢣⣿⣿⠉⠀⣠⣾⣿⣿⡿⣣⣿⣿⡿⣿⣿⣿⡿⣱⣿⣿⣿⡟⣼⣿⢿⣿⡿⣿⣿⣿⣧⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⡿⣯⢞⣼⣿⣟⣵⣿⣯⣿⣿⠿⣠⣾⣿⣿⣿⡟⣱⣿⣿⣿⣿⣶⣽⢿⣾⣿⣿⣿⡿⢹⣿⣳⡿⣫⣾⣿⣿⣿⡿⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⢳⣿⢸⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⠾⠿⢏⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⠟⣼⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⣵⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣇⣿⣵⣟⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡟⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⡿⣼⡿⣸⣿⡿⠿⠛⠉⢀⣴⣿⣿⡿⢛⣼⠆⣾⣿⡿⣿⣿⣿⢟⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⢯⣶⡟⣨⣥⣖⠁⠀⠀⢠⣿⡿⢟⣷⣾⣿⢏⣼⣿⣿⣿⣦⣟⣽⣿⡟⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡇⢹⣿⡿⢿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣵⡿⢋⣴⣿⡿⠀⠀⠀⣀⣿⣭⣾⣿⣿⣿⢏⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⢋⣽⣿⣿⣧⢹⣿⣿⢿⣡⡾⡃⣾⣿⡔⣋⣙⣟⣙⣿⣿⡇⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣷⣿⣿⡿⠃⠀⠀⠀⣟⣫⢿⣿⣿⣿⡟⣼⣿⣿⣎⡽⣵⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡷⣯⣾⢿⣿⣿⡧⢹⡿⣫⣥⣯⣭⣿⣿⣿⡇⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⡿⠁⠀⢤⣶⡆⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⣸⣿⣿⣿⢯⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡿⣛⣫⣼⣿⣿⣿⠇⣼⣿⣶⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⡏⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
System.out.println("⣿⣿⣿⡇⣨⣷⣿⣿⣿⠸⣿⣿⣿⣿⢣⣿⣶⣧⢷⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣯⠛⢋⣡⣴⣽⣿⣯⣭⣭⣭⣭⣿⣿⡇⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿");
}
/**
* A Java Driver/Test method that is the entry point for execution
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MonkeyLoop().printPoem(); //a new monkey list and output in one step
}
}
MonkeyLoop.main(null);
/*
* Creator: Nighthawk Coding Society
* Mini Lab Name: Fibonacci sequence, featuring a Stream Algorithm
*
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/* Objective will require changing to abstract class with one or more abstract methods below */
public class Fibo {
String name; // name or title of method
int size; // nth sequence
int hashID; // counter for hashIDs in hash map
ArrayList<Long> list; // captures current Fibonacci sequence
HashMap<Integer, Object> hash; // captures each sequence leading to final result
/*
Zero parameter constructor uses Telescoping technique to allow setting of the required value nth
@param: none
*/
public Fibo() {
this(20); // telescope to avoid code duplication, using default as 20
}
/*
Construct the nth fibonacci number
@param: nth number, the value is constrained to 92 because of overflow in a long
*/
public Fibo(int nth) {
this.size = nth;
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
this.hashID = 0;
this.hash = new HashMap<>();
//initialize fibonacci and time mvc
this.init();
}
/*
This Method should be "abstract"
Leave method as protected, as it is only authorized to extender of the class
Make new class that extends and defines init()
Inside references within this class would change from this to super
Repeat process using for, while, recursion
*/
protected void init() {
this.name = "Stream";
Stream.iterate(new long[]{0, 1}, f -> new long[]{f[1], f[0] + f[1]})
.limit(this.size)
.forEach(f -> this.setData(f[0]) );
}
/*
Number is added to fibonacci sequence, current state of "list" is added to hash for hashID "num"
*/
public void setData(long num) {
list.add(num);
hash.put(this.hashID++, list.clone());
}
/*
Custom Getter to return last element in fibonacci sequence
*/
public long getNth() {
return list.get(this.size - 1);
}
/*
Custom Getter to return last fibonacci sequence in HashMap
*/
public Object getNthSeq(int i) {
return hash.get(i);
}
/*
Console/Terminal supported print method
*/
public void print() {
System.out.println("Init method = " + this.name);
System.out.println("fibonacci Number " + this.size + " = " + this.getNth());
System.out.println("fibonacci List = " + this.list);
System.out.println("fibonacci Hashmap = " + this.hash);
for (int i=0 ; i<this.size; i++ ) {
System.out.println("fibonacci Sequence " + (i+1) + " = " + this.getNthSeq(i));
}
}
/*
Tester class method. If this becomes abstract you will not be able to test it directly ...
Change this method to call "main" class of each of the extended classes
*/
static public void main(String[] args) {
Fibo fib = new Fibo();
fib.print();
}
}
Fibo.main(null);
In the code below, I create a new class called ForFibo that extends the original Fibo class.(means it can use all attributes of Fibo class) I use super() to change this.size from 20 to 10.
Then I using super.name to change this.name to "For loop example" so when I print out the method name it will print out this string.
I create a new class init2(), inside the class is the for loop that use to print out the fibonacci number from 0 to 10.
public class ForFibo extends Fibo{
public ForFibo(){
super(10);
}
int forn1 = 0;
int forn2 = 0;
int forn3 = 0;
protected void init2() {
super.name = "For loop example";
System.out.println("Init method = " + super.name);
for (int n=0 ; n<=super.size; n++ ){
forn3 = (forn1 + forn2);
System.out.println(n + "th fibonacci number is: " + forn3);
forn1 = forn2;
forn2 = forn3;
if (n < 2){
forn2 = 1;
forn1 = 0;
}
}
}
static public void main(String[] args) {
ForFibo fib = new ForFibo();
fib.init2();
}
}
ForFibo.main(null);
Then for the while loop, there is similar between the for loop and while loop. Both need to contain condition and both run until the condition is not true. So basically I just need to keep the main part of code and change few thing to make it work.
public class WhileFibo extends Fibo{
public WhileFibo(){
super(10);
}
int whilei = 0;
int whilei2 = 0;
int forn1 = 0;
int forn2 = 0;
int forn3 = 0;
protected void init3() {
super.name = "While loop example";
System.out.println("Init method = " + super.name);
while (whilei2<=super.size){
forn3 = (forn1 + forn2);
System.out.println(whilei2 + "th fibonacci number is: " + forn3);
forn1 = forn2;
forn2 = forn3;
if (whilei2 < 2){
forn2 = 1;
forn1 = 0;
}
whilei2 += 1;
}
}
static public void main(String[] args) {
WhileFibo fib = new WhileFibo();
fib.init3();
}
}
WhileFibo.main(null);
And also for the while loop, because it can only contain the condition inside the parenthesis(it can't create a value) So I create set a new value above the while loop.
int whilei = 0;
int whilei2 = 0;
int forn1 = 0;
int forn2 = 0;
int forn3 = 0;
Last, for the recursion, I create a new class called recu(), inside the class is the code that define the fibonacci by using recursion.
If the input number is greater and equal to 2, then it will return the fibonacci for the number.
If the number is less than 2 such as 1 and 0, it will just print out the input number which is also the same as the fibonacci It should has.
If the number is less than 0(negative), it will print out the number and also warm you that you shouldn't input a negative number.
public class ReFibo extends Fibo{
public ReFibo(){
super(20);
}
static long recu(long n) {
if (n >= 2)
return recu(n - 1) + recu(n - 2);
else
return n;
}
int forn1 = 0;
int forn2 = 0;
int forn3 = 0;
protected void init4() {
super.name = "Recursion example";
System.out.println("Init method = " + super.name);
for (int n=0 ; n<=super.size; n++ ) {
System.out.println(n + "th fibonacci number is: " + recu(n));
if (n < 0){
System.out.println("You shouldn't input a negative number!!");
}
}
}
static public void main(String[] args) {
ReFibo fib = new ReFibo();
fib.init4();
}
}
ReFibo.main(null);
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
//RapidAPI header https://rapidapi.com/spamakashrajtech/api/corona-virus-world-and-india-data
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://spoonacular-recipe-food-nutrition-v1.p.rapidapi.com/recipes/complexSearch"))
.header("x-rapidapi-key", "a5693b4414msh85cfb00ddeafe1cp1631ecjsnd910ff3015d0")
.header("x-rapidapi-host", "spoonacular-recipe-food-nutrition-v1.p.rapidapi.com")
.method("GET", HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.noBody())
.build();
//RapidAPI request and response
HttpResponse<String> response = HttpClient.newHttpClient().send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
//RapidAPI Body
System.out.println(response.body());
Q: Benefit of using and API?
A:
For me, It is easier to find and publish the information to the page. It help us to save time in finding information and coding, especially for some data that is updated all the time like the covid or airplane.
package com.nighthawk.spring_portfolio.mvc.covid;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController // annotation to create a RESTful web services
@RequestMapping("/api/covid") //prefix of API
public class CovidApiController {
private JSONObject body; //last run result
private HttpStatus status; //last run status
String last_run = null; //last run day of month
// GET Covid 19 Stats
@GetMapping("/daily") //added to end of prefix as endpoint
public ResponseEntity<JSONObject> getCovid() {
//calls API once a day, sets body and status properties
String today = new Date().toString().substring(0,10);
if (last_run == null || !today.equals(last_run))
{
try { //APIs can fail (ie Internet or Service down)
//RapidAPI header
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://corona-virus-world-and-india-data.p.rapidapi.com/api"))
.header("x-rapidapi-key", "dec069b877msh0d9d0827664078cp1a18fajsn2afac35ae063")
.header("x-rapidapi-host", "corona-virus-world-and-india-data.p.rapidapi.com")
.method("GET", HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.noBody())
.build();
//RapidAPI request and response
HttpResponse<String> response = HttpClient.newHttpClient().send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
//JSONParser extracts text body and parses to JSONObject
this.body = (JSONObject) new JSONParser().parse(response.body());
this.status = HttpStatus.OK; //200 success
this.last_run = today;
}
catch (Exception e) { //capture failure info
HashMap<String, String> status = new HashMap<>();
status.put("status", "RapidApi failure: " + e);
//Setup object for error
this.body = (JSONObject) status;
this.status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR; //500 error
this.last_run = null;
}
}
//return JSONObject in RESTful style
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
}
Q: Benefit(s) of backend implementation?
A: I can't run this code in jupyter notebook so I don't exactly what the benefits. But I read the comment. It seems like the backend implementation will reload the API everyday(to get the newest information) and help to save our time and also help us to organize.
Hacks
Continue to work with Classes, Arrays, and 2D arrays. FYI, you may need to make a directory /tmp under notebook images.
Look at comments above and see if there is better conversions for ASCII to reduce elongation and distortion.
Try to convert images into Grey Scale, Red Scale, Blue Scale, and Green Scale.
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
public class ImageIOTest {
public static void main( String[] args ){
BufferedImage img = null; // buffer type
try {
// Name of file and directories
String name = "MonaLisa";
String in = "images/";
String out = "images/tmp/";
// Either use URL or File for reading image using ImageIO
File imageFile = new File(in + name + ".png");
img = ImageIO.read(imageFile); // set buffer of image data
// ImageIO Image write to gif in Java
// Documentation https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/2d/images/index.html
ImageIO.write(img, "gif", new File(out + name + ".gif") ); // write buffer to gif
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Success");
}
}
ImageIOTest.main(null);
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import javax.imageio.stream.ImageOutputStream;
import javax.imageio.stream.ImageInputStream;
import javax.imageio.metadata.IIOMetadata;
import javax.imageio.IIOImage;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.imageio.ImageWriteParam;
import javax.imageio.ImageWriter;
import javax.imageio.ImageReader;
import javax.imageio.ImageTypeSpecifier;
public class Pics {
private final String inDir = "images/"; // location of images
private final String outDir ="images/tmp/"; // location of created files
private String inFile;
private String resizedFile;
private String asciiFile;
private String ext; // extension of file
private long bytes;
private int width;
private int height;
// Constructor obtains attributes of picture
public Pics(String name, String ext) {
this.ext = ext;
this.inFile = this.inDir + name + "." + ext;
this.resizedFile = this.outDir + name + "." + ext;
this.asciiFile = this.outDir + name + ".txt";
this.setStats();
}
// An image contains metadata, namely size, width, and height
public void setStats() {
BufferedImage img;
try {
Path path = Paths.get(this.inFile);
this.bytes = Files.size(path);
img = ImageIO.read(new File(this.inFile));
this.width = img.getWidth();
this.height = img.getHeight();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
// Console print of data
public void printStats(String msg) {
System.out.println(msg + ": " + this.bytes + " " + this.width + "x" + this.height + " " + this.inFile);
}
// Convert scaled image into buffered image
public static BufferedImage convertToBufferedImage(Image img) {
// Create a buffered image with transparency
BufferedImage bi = new BufferedImage(
img.getWidth(null), img.getHeight(null),
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
// magic?
Graphics2D graphics2D = bi.createGraphics();
graphics2D.drawImage(img, 0, 0, null);
graphics2D.dispose();
return bi;
}
// Scale or reduce to "scale" percentage provided
public void resize(int scale) {
BufferedImage img = null;
Image resizedImg = null;
int width = (int) (this.width * (scale/100.0) + 0.5);
int height = (int) (this.height * (scale/100.0) + 0.5);
try {
// read an image to BufferedImage for processing
img = ImageIO.read(new File(this.inFile)); // set buffer of image data
// create a new BufferedImage for drawing
resizedImg = img.getScaledInstance(width, height, Image.SCALE_SMOOTH);
} catch (IOException e) {
return;
}
try {
ImageIO.write(convertToBufferedImage(resizedImg), this.ext, new File(resizedFile));
} catch (IOException e) {
return;
}
this.inFile = this.resizedFile; // use scaled file vs original file in Class
this.setStats();
}
// convert every pixel to an ascii character (ratio does not seem correct)
public void convertToAscii() {
BufferedImage img = null;
PrintWriter asciiPrt = null;
FileWriter asciiWrt = null;
try {
File file = new File(this.asciiFile);
Files.deleteIfExists(file.toPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Delete File error: " + e);
}
try {
asciiPrt = new PrintWriter(asciiWrt = new FileWriter(this.asciiFile, true));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("ASCII out file create error: " + e);
}
try {
img = ImageIO.read(new File(this.inFile));
} catch (IOException e) {
}
for (int i = 0; i < img.getHeight(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < img.getWidth(); j++) {
Color col = new Color(img.getRGB(j, i));
double pixVal = (((col.getRed() * 0.30) + (col.getBlue() * 0.59) + (col
.getGreen() * 0.11)));
try {
asciiPrt.print(asciiChar(pixVal));
asciiPrt.flush();
asciiWrt.flush();
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
try {
asciiPrt.println("");
asciiPrt.flush();
asciiWrt.flush();
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
}
// conversion table, there may be better out there ie https://www.billmongan.com/Ursinus-CS173-Fall2020/Labs/ASCIIArt
public String asciiChar(double g) {
String str = " ";
if (g >= 240) {
str = " ";
} else if (g >= 210) {
str = ".";
} else if (g >= 190) {
str = "*";
} else if (g >= 170) {
str = "+";
} else if (g >= 120) {
str = "^";
} else if (g >= 110) {
str = "&";
} else if (g >= 80) {
str = "8";
} else if (g >= 60) {
str = "#";
} else {
str = "@";
}
return str;
}
// tester/driver
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Pics monaLisa = new Pics("MonaLisa", "png");
monaLisa.printStats("Original");
monaLisa.resize(33);
monaLisa.printStats("Scaled");
monaLisa.convertToAscii();
Pics pumpkin = new Pics("pumpkin", "png");
pumpkin.printStats("Original");
pumpkin.resize(33);
pumpkin.printStats("Scaled");
pumpkin.convertToAscii();
}
}
Pics.main(null);
I can't run the code, but I have the idea of how to add red, green, blue scale. The key is to change the RGB value. EX. For red scale, change the R value to max ( using col.getRed() instead of using col.getRed() * 0.30 ), and change the G, B value to 0.
// gray scale
Color col = new Color(img.getRGB(j, i));
double pixVal = (((col.getRed() * 0.30) + (col.getBlue() * 0.59) + (col
.getGreen() * 0.11)));
// red scale
Color col = new Color(img.getRGB(j, i));
double pixVal = ((col.getRed() + 0 + 0));
// Java Program to Demonstrate
// Working of an ArrayList class
// Importing all classes from java.util package
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.Math;
// Main class
class NBAPlayers {
// Main driver method
public static void main()
{
ArrayList<String> namePlayer = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<Integer> CEPlayer = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Random random = new Random();
namePlayer.add("Boban Marjanovic");
namePlayer.add("Sim Bhullar");
namePlayer.add("Tacko Fall");
namePlayer.add("Pavel Podkolzin");
namePlayer.add("Chuck Nevitt");
namePlayer.add("Yao Ming");
namePlayer.add("Shawn Bradley");
namePlayer.add("Manute Bol");
namePlayer.add("Gheorghe Muresan");
System.out.println("Top 9 tallest NBA players:");
System.out.println(namePlayer);
System.out.println();
int min = 0;
int max= namePlayer.size();
int ranNum1 = random.nextInt(max);
int ranNum2 = random.nextInt(max);
int ranCE1 = random.nextInt(100);
int ranCE2 = random.nextInt(100);
CEPlayer.add(ranCE1);
CEPlayer.add(ranCE2);
System.out.println("1 vs 1 game !");
System.out.println();
System.out.println(namePlayer.get(ranNum1) + " vs " + namePlayer.get(ranNum2));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Their Combat Effectiveness:");
System.out.println(CEPlayer);
System.out.println();
if (ranCE1 > ranCE2 ){
System.out.println(namePlayer.get(ranNum2) + " lose the game");
namePlayer.remove(ranNum2);
}
else if (ranCE2 > ranCE1){
System.out.println(namePlayer.get(ranNum1) + " lose the game");
namePlayer.remove(ranNum1);
}
else if (ranCE2 == ranCE1){
System.out.println("Tie!");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Now, there are only " + namePlayer.size() + " players");
System.out.println(namePlayer);
}
}
NBAPlayers.main();
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Data // Annotations to simplify writing code (ie constructors, setters)
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity // Annotation to simplify creating an entity, which is a lightweight persistence domain object. Typically, an entity represents a table in a relational database, and each entity instance corresponds to a row in that table.
public class Jokes {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id; // Unique identifier
@Column(unique=true)
private String joke; // The Joke
private int haha; // Store joke likes
private int boohoo; // Store joke jeers
}
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Data // Annotations to simplify writing code (ie constructors, setters)
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity // Annotation to simplify creating an entity, which is a lightweight persistence domain object. Typically, an entity represents a table in a relational database, and each entity instance corresponds to a row in that table.
public class Jokes {
private Long id; // Unique identifier
private String joke; // The Joke
private int haha; // Store joke likes
private int boohoo; // Store joke jeers
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getjoke() {
return joke;
}
public void setjoke(String joke) {
this.joke = joke;
}
public int gethaha() {
return haha;
}
public void sethaha(int haha) {
this.haha = haha;
}
public int getboohoo() {
return boohoo;
}
public void setboohoo(int boohoo) {
this.boohoo = boohoo;
}
}
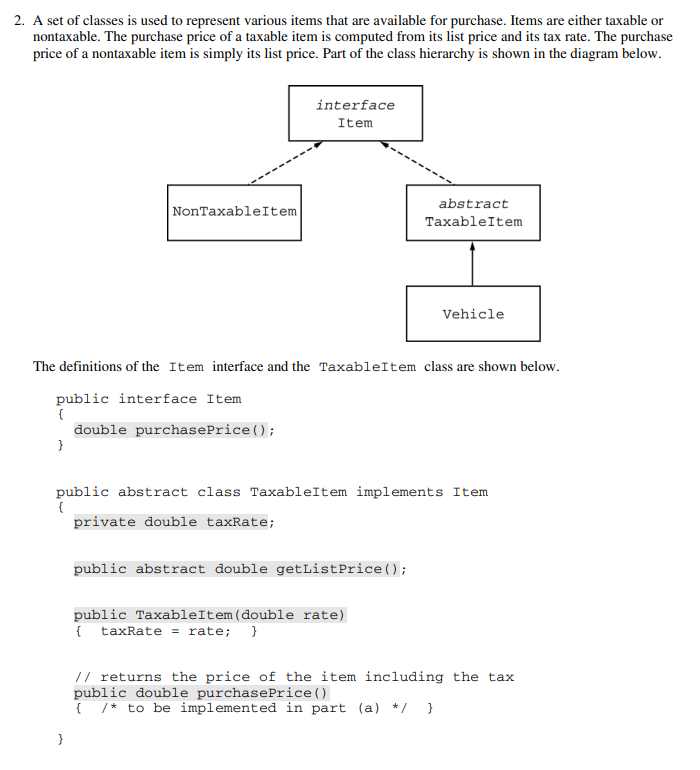
part 2a
public double purchasePrice(){
double taxableitem = getListPrice + (getListPrice * rate);
// the purchase price of a taxableitem is its list price plus the tax on the item.
// but because in the origin class (getListPrice()) is empty so I guess it will provide the value.
return taxableitem;
}


part 3a
Customer c1 = new Customer("Smith", 1001);
Customer c2 = new Customer("Anderson", 1002);
Customer c3 = new Customer("Smith", 1003);
public int compareCustomer (Customer other){
if ( > ){ // I don't know how to add the condition that shows the chosen object is greater than the input
String integer = "a positive integer";
return integer;
}
else if ( < ){ //same
String integer = "a negative integer";
return integer;
}
else {
return 0
}
}
class MonkeyLoop {
//The area between class definition and the 1st method is where we keep data for object in Java
String [][] monkeys; //2D Array: AP CSA Unit 8: 2D array of strings
//2D array is like a grid [x][y]
// or like a spreadsheet [row][column]
String [][] cthulhus;
public MonkeyLoop() {
//Storing Data in 2D arrays
monkeys = new String[][]{ //2D array above is just a name, "new" makes a container ("object")
{
"ʕง ͠° ͟ل͜ ͡°)ʔ ", //[0][0] eyes
},
{
" \\_⏄_/ ", //[1][0] chin
},
{
" --0-- ", //[2][0] body
},
{
" ⎛ ⎞ " //[3][0] legs
},
};
cthulhus = new String[][]{
{
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⡠⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢎⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ʕง ͠° ͟ل͜ ͡°)ʔ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠂⢱⠀⠀⢀⣤⡀⠀⠀⢣⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ \\_⏄_/ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⣰⠻⠉⣧⣿⣿⣿⠀⠀⢸⠇⠀⠐⠉⡆⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ --0-- ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⠔⠒⢦⠀⢻⡄⠀⢿⣻⣿⡿⢀⣴⣋⣄⣄⣌⣠⠃⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ⎛ ⎞ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠀⢀⡞⠀⠈⠛⣷⣾⣿⣿⣿⣿⣿⣯⣥⣀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠈⠷⣦⣴⡾⢿⣿⡿⢿⣿⣋⣽⠶⢦⠙⢷⡀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢀⣾⡏⢀⡆⠈⠉⠁⡄⠈⡇⠘⢇⠀⢈⡆⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⢸⡯⠀⠸⠁⠀⠀⠸⣧⡀⡇⠀⠈⠉⠉⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ ",
"⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠸⣇⡴⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠙⠛⠁⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ "
},
};
}
public void printPoem() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("A story of a Monkey and Cthulhus");
int Crow = 0;
int monkeyCount = monkeys.length;
for (int i = monkeyCount; i >= 1; i--)
{
for (int row = 0; row < monkeyCount; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < monkeys[row].length; col++) {
System.out.print(monkeys[row][col] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
monkeyCount = 0;
}
for (int Ccol = 0; Ccol < cthulhus[Crow].length; Ccol++) {
System.out.print(cthulhus[Crow][Ccol] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("0000000000000000000000000000000000");
System.out.println(" THE END ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MonkeyLoop().printPoem();
}
}
MonkeyLoop.main(null);


public class FRQ1 {
public static int numberOfLeapYears(int year1, int year2) { //create a static method
boolean isLeapYear = false; //create a boolean called isLeapYear
for(int i = year1 ; i <= year2 && i > 0; i++)
{
if (i % 4 ==0){ //determine if i(year) is or not a leap year
if (i % 100 == 0){
if (i % 400 == 0){
isLeapYear = true;
}
else {
isLeapYear = false;
}
}
else isLeapYear = true;
}
else isLeapYear = false;
if (isLeapYear){ //method that if the boolean is true(if i is a leap year), print the year
System.out.println(i + " is a leap year.");
}
}
return year1; //return code (no actual use, just to make sure the class goes well)
}
}
FRQ1.numberOfLeapYears(1900, 2000);

public class FRQ1 {
private static int firstDayOfYear(int year){
//helper method
}
public static int dayOfweek(int month, int day, int year) {
int firstDay = firstDayOfYear(year);
int doy = dayOfYear(month, day, year);
return (firstDay + doy - 1) % 7;
}
}
FRQ1.dayOfweek(1, 10, 2019);
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.Math;
public class IterationHW {
public static int guess(int num) { //create a static method
Random random = new Random();
int ranNum = random.nextInt(10);
boolean greater;
boolean less;
if (num > ranNum ){
System.out.println("Your Guess: " + num + " ,is greater than number");
greater = true;
less = false;
}
else if (num < ranNum){
System.out.println("Your Guess: " + num + " ,is less than number");
greater = false;
less = true;
}
else if (num == ranNum){
greater = true;
less = true;
}
if (greater && less){
System.out.println("You find the number");
}
return ranNum;
}
}
IterationHW.guess(1);
public class Goblin {
private String name;
private int HP;
private int DMG;
private double hitChance;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getHP() {
return HP;
}
public int getDMG() {
return DMG;
}
public double getHitChance() {
return hitChance;
}
public boolean isAlive() {
if (this.HP > 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public void setName(String newName) {
this.name = newName;
}
public void setHP(int newHP) {
this.HP = newHP;
}
public void takeDMG(int takenDamage) {
this.HP -= takenDamage;
}
public void setDMG(int newDMG) {
this.DMG = newDMG;
}
public void setHitChance(double newHitChance) {
this.hitChance = newHitChance;
}
}
import java.lang.Math;
public class Duel {
public static void attack(Goblin attackerGoblin, Goblin attackeeGoblin) {
System.out.println(attackerGoblin.getName() + " attacks " + attackeeGoblin.getName() + "!");
if (Math.random() < attackerGoblin.getHitChance()) {
attackeeGoblin.takeDMG(attackerGoblin.getDMG());
System.out.println(attackerGoblin.getName() + " hits!");
System.out.println(attackeeGoblin.getName() + " takes " + attackerGoblin.getDMG() + " damage");
} else {
System.out.println(attackerGoblin.getName() + " misses...");
}
System.out.println(attackeeGoblin.getName() + " HP: " + attackeeGoblin.getHP());
System.out.println();
}
public static void fight(Goblin goblin1, Goblin goblin2) {
while (goblin1.isAlive() && goblin2.isAlive()) {
attack(goblin1, goblin2);
if (!goblin1.isAlive()) {
System.out.println(goblin1.getName() + " has perished");
break;
}
attack(goblin2, goblin1);
if (!goblin2.isAlive()) {
System.out.println(goblin2.getName() + " has perished");
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Goblin goblin1 = new Goblin();
goblin1.setName("jeffrey");
goblin1.setHP(12);
goblin1.setDMG(2);
goblin1.setHitChance(0.50);
Goblin goblin2 = new Goblin();
goblin2.setName("Gunther the great");
goblin2.setHP(4);
goblin2.setDMG(1);
goblin2.setHitChance(1);
fight(goblin1, goblin2);
}
}
Duel.main(null);
1a

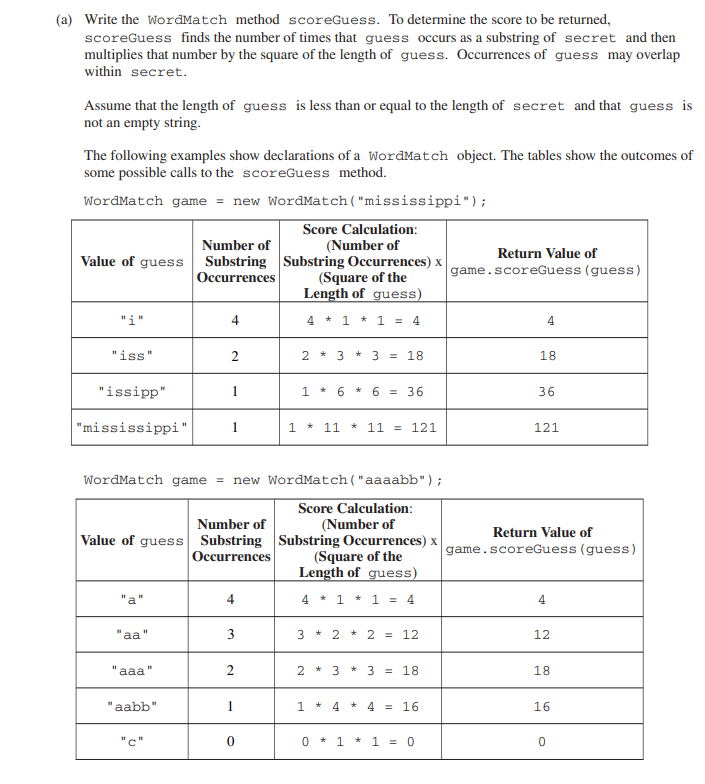
public int scoreGuess(String guess){
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < secret.length(); i++){
if(secret.substring(i).indexOf(guess) == 0){
result++;
}
}
return result * guess.length() * guess.length();
3a


public void addMembers (String[] names, int gradYear){
for (String n : names)
{
MemberInfo newM = new MemberInfo (n, gradYear, true);
memberList.add(newM);
}
}
public static int dayOfWeek(int month, int day, int year) {
// to be implemented in part (b)
// math function: w=(k+[2.6m-0.2]-2c+Y+[Y/4]+[C/4])%7
double week;
double c = Math.floor(year/100);
double Y = year - (c * 100);
int month1 = 0;
double year1 = 0;
if (month == 1 || month == 2){
month1 += (month + 10);
year1 += (Y -1);
}
else {
month1 += (month - 2);
year1 += Y;
}
week = ((day + Math.floor(2.6 * month1 - 0.2) - 2*c + year1 + Math.floor(year1/4)+ Math.floor(c/4))%7);
int weekday = (int) Math.round(week);
return weekday;
}
Unit 07 - ArrayList HW
Sort an ArrayList in descending order and swap the first and last elements
Find and display the hashCode of an Arraylist before and after being sorted
Return "ascending" if the list is sorted in ascending order, return "descending" if it is descending, and return "neither" if neither
Replace 3 elements in an ArrayList with another ArrayList and reverse the order of the new list
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.Math;
ArrayList<Integer> number = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Integer> number2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
number.add(i);
}
for (int i = 5; i > 0; i--){
number.add(i);
}
System.out.println("Original: " +number);
System.out.println("HashCode: " + number.hashCode());
number.sort(Comparator.reverseOrder());
System.out.println("ArrayList after sort: " + number);
System.out.println("HashCode: " + number.hashCode());
Collections.swap(number, 4, 0);
System.out.println("Swap the first and last elements: " + number);
System.out.println("HashCode: " + number.hashCode());
boolean a;
boolean b;
for (int i=0; i < number.size() - 1; i++){
if (!(number.get(i) <= number.get(i + 1))){
boolean a = false;
}
if (!(number.get(i) >= number.get(i + 1))){
boolean b = false;
}
}
if (a){
System.out.println("ascending");
}
if (b){
System.out.println("descending");
}
else{
System.out.println("neither");
}
public class LightBoard{
private boolean[][] lights;
public LightBoard (int numRows, int numCols){
lights = new boolean [numRows][numCols];
for (int row = 0; row < lights.length; row++){
for (int col = 0; col < lights[row].length; col++){
if(Math.random() <= 0.4){
lights[row][col] = true;
}
}
}
}
public boolean evaluateLight(int row, int col){
for(int r = 0; r < lights.length; r++){
for(int c = 0; col < lights[row].length; col++){
if(lights[r][c] == true)
{
if(c % 2 == 0){
return false;
}
}
else
{
if(c % 3 == 0){
return true;
}
}
}
}
return lights[r][c];
}
static public void main(String[] args) {
// create and display LightBoard
LightBoard lightBoard = new LightBoard(5, 5);
System.out.println(lightBoard); // use toString() method
System.out.println(lightBoard.evaluateLight(5, 5));
}
}
public class Worldcup {
private String name;
public Worldcup(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return (this.name);
}
}
public class team1 extends Worldcup {
public team1(String name){
super(name); // call superclass constructor
}
}
public class team2 extends Worldcup {
//similar code like team1
}
public class team3 extends Worldcup {
//similar code like team1
}
public class team4 extends Worldcup {
//similar code like team1
}
public class team5 extends Worldcup {
//similar code like team1
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Team1 team1 = new Team1("I don't know any name of the Worldcup teams")
System.out.println("Team name: " + team1);
}
public class Person {
private String name;
private String birthday;
private int age;
public Person (String name, String birthday, int age){
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public String getBirthday(){
return birthday;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public String toString(){
return("Name: " + this.getName() + ", Birthday: " + this.getBirthday() + ", Age: " + this.getAge());
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
private int grade;
private double gpa;
public Student (String name, String birthday, int grade, double gpa, int age) {
super(name, birthday, age);
this.grade = grade;
this.gpa = gpa;
}
public int getGrade(){
return grade;
}
public Double getGpa(){
return gpa;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return("Name: " + this.getName() + ", Birthday: " + this.getBirthday() + ", Age: " + this.getAge() + ", Grade: " + this.getGrade() + ", GPA: " + this.getGpa());
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person {
private String sub;
public Teacher (String name, String birthday, int age, String sub) {
super(name, birthday, age);
this.sub = sub;
}
public String getSub(){
return sub;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return("Name: " + this.getName() + ", Birthday: " + this.getBirthday() + ", Age: " + this.getAge() + ", Subject: " + this.getSub());
}
}
public class Homework{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("Tianbin", "2018-05-05", 12);
System.out.println("Person: " + person);
Student student = new Student("Tianbin", "2005-04-28", 11, 4.9, 17);
System.out.println("Student: " + student);
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("Mr. M", "1000-10-10", 45, "Computer Science A");
System.out.println("Teacher: " + teacher);
}
}
Homework.main(null);
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayMethods {
private int[] values = {1,2,3,4,5};
public void swapFirstAndLast(){
int lastElement = values[values.length-1];
values[values.length-1] = values[0];
values[0] = lastElement; //Resource found right herehttps://stackoverflow.com/questions/40567582/swap-first-and-last-value-in-an-array-java
}
public void zero(){
for(int i = 0; i < values.length; i++){
values[i] = 0;
}
}
public String toString(){
return Arrays.toString(values);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayMethods swapFAL = new ArrayMethods();
swapFAL.swapFirstAndLast();
System.out.println(swapFAL.toString());
swapFAL.zero();
System.out.println(swapFAL.toString());
}
}
ArrayMethods.main(null);
//resource come from https://www.java67.com/2018/05/coding-2-ways-to-add-binary-numbers-in-Java.html
int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 1;
Integer num= new Integer(num1 + num2);
Integer.toBinaryString(num);